stream 스트림 사용예시 모음
mission간 stream관련 사용예시 모음
📜 제목으로 보기
- Stream 기본
- 프리코스때 한 것
- .filter() 신기한 것
- 이중반복문
- 외부List.of()를 배려한 가변인자(배열)의 내부처리는 stream보다는 List.of()
- 같은Type에 대해 일괄처리: List.of로 담아 + stream.일괄처리 —> Stream.of().일괄처리
- 반복문iter와 forEach
- 반복문fori 과 IntStream
- 집계max( 숫자VO::compareTo )
- list필터링- filter ( -> 객체. t/f반환메서드 사용 )
- 특정 문자열속성 joinning - (map+getString -> joining)
- 만족하는 총 갯수 카운팅(for+if+add ->) by filter.() + (다모아서) count()
- 역순 list
- 역순 stream With comparable 상속
- 누적은 mapToType + .집계 » .reduce(초기값, 해당Type::집계함수) 더 깔끔
- toSet() / toMap() 등… 다른 것으로도 가능
- contains와 anyMatch or noneMatch & equals(같은게 & 하나라도 있냐)
- 해당(포함)하는게 있으면 -> 찾아서 -> 특정 로직 수행까지 진행된다면, anyMatch + 비교메서드가 아니라 filter + findAny 찾아놓고 -> ifPresent( -> 수행메서드() )로 다르게 작성한다.
- 로또
- 블랙잭
- 로또
- 체스
- 지하철 경로
Stream 기본
프리코스때 한 것
-
String 역 출력 -> new StringBuilder( string ) .reverse().toString() -> split -> stream -> list -> Collections.reverse( list )가 inplace 역순시킨다. -> stream + reduce + get으로 문자열 모으기
-
arr 2개 합치기 -> Stream.of( arr1, arr2) .flatMap(Stream::of) .collect(Collectors.toList());
-
list 2개 합치기 ( stream없이 할려면, 빈리스트에 addAll + addAll ) -> Stream.concat( list1.stream(), list2.stream())
-
list 중복제거 -> list.stream().distinct() + .collect(Collectors.toList())
-
list의 집계함수 만들기 by reduce().get() + Integer::sum -> list.stream() .reduce(Integer::sum) .get();
-
음수검사: IntStream만들어서 custom boolean식 만들고 filter에 넣기 -> Arrays.stream(mathexpression.split(“,|:”)) .mapToInt(Integer::parseInt) .filter(i -> checkNegative(i)) // .sum();
-
숫자사이 연산자들의 연속입력 검사 : -> if (Arrays.stream(removedSpaceInput.split(“[0-9]”)).anyMatch(operator -> operator.length() > 1)) {
-
객체속 변수2개로 -> map key, value만들기 -> list.stream() // .sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Item::getId).reversed()) .collect(Collectors.toMap( Item::getId, Item::getValue, (OldId, newId) -> OldId, // (OldId, newId) -> newId, LinkedHashMap::new ));
.filter() 신기한 것
-
anyMatch 류는 해당하는 것들만 필터링 된다.
-
string을 돌고 있다면, str.indexOf(“특정문자”) == 2 등과 같이 특정문자열 1개의 위치로 필터링 가능하다
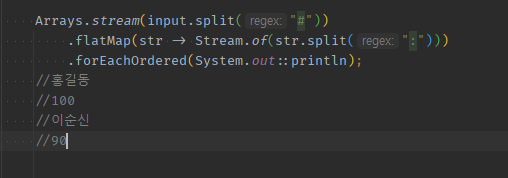
Arrays.stream(input.split("#")) // 홍길동:100 , 이순신:90 .flatMap(str -> Stream.of(str.split(":"))) // {홍길동, 100} , {이순신,90} -> 홍길동,100,이순신,90 .filter(it -> it.indexOf("신") == 2) .findFirst() .ifPresent(s-> System.out.println(s)); -
null아닌 것만 필터링 하려면 Objects.notnull()을 필터에 넣어주면 된다.
Collection<String> animals = Arrays.asList("Dog", "Cat", null, "Moose"); String result = animals.stream() .filter(Objects::nonNull) .collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
이중반복문
이중반복문 + 조건식 -> 요소1vs요소2 필터링 by .filter( .anyMatch() )
-
java8이전
final List<String> abcde = List.of("a", "b", "c", "d", "e"); final List<String> abd = List.of("a", "b", "d"); // 8이전: 이중 for문 + 조건식 -> 반복문내 조건만족값을 모을 결과값 가변변수에 add final List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); for (final String str1 : abcde) { for (final String str2 : abd) { if (str1.equals(str2)) { result.add(str1); // 같으니까 둘중에 하나만 담기 } } } System.out.println("result = " + result); //result = [a, b, d] -
java8 Stream
- 바깥Stream.filter() + 안쪽Stream.anyMatch()
//1. 첫번째 list를 돌 때, 2번째 list가 돌았다고 가정하고 둘이서 condition조건식을 비교하므로 // -> .map()이나 .collect()가 아닌 .filter( 1stElement -> )로 시작하는 것을 유의해야한다. // -> my) 돌면서 조건식 -> stream().filter() //.filter( str1 -> str1) //2. 람다식 -> 우측에는 1번째 요소 이전에 2번째 list가 먼저 stream으로 풀어져야하므로, list2부터등장하는 것을 유의해야한다. //.filter( str1 -> abd.stream(). ) // -> 2list.stream()이후 2번째 요소가 등장한다고 가정하면, 뭘 할 것인가 를 먼저 생각하고 .메서드()를 호출해야한다. // -> .stream(). ??? ( 2번재요소 -> 1번째요소랑 .equals()등의 조건식을 다룰 것)이므로 // --> 2번째 stream의 요소는 조건식인 anyMatch/allMatch/noneMatch( ) 내부에서 1번째 요소를 맞이한다. // --> 이후 filter( 내부에서 해당 조건식을 통과하는 것만 남겨진다.) final List<String> result2 = abcde.stream() .filter(str1 -> abd.stream() // .( str2 -> str2.equals(str1)) .anyMatch(str2 -> str2.equals(str1))) // str1 1개에 대해, list2 중에 어느하나라도 만족한다면, 통과? // -> filter( anyMatch( 조건식 )-> 어느하나라도?(X) 만족하는 것만 필터링한다** // --> filter( noneMatch( 조건식 ) ->모두불만족시 true?(X) 불일치하는 것만 필터링** .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); //result2 = [a, b, d] //암기하자면 - list1 + list2 + 조건식이다? //list1.stream().filter()로 시작하여 e1은 결국 e2와 조건식을 비교해서 if필터링해서 모아야한다. //list2.stream().anyMatch( e2 -> e1과조건식)으로 [조건을 만족하는 데이터만 true체크]한 뒤, filter로 넘어갈 수 있게 한다. //모은다. result2.forEach(System.out::print);
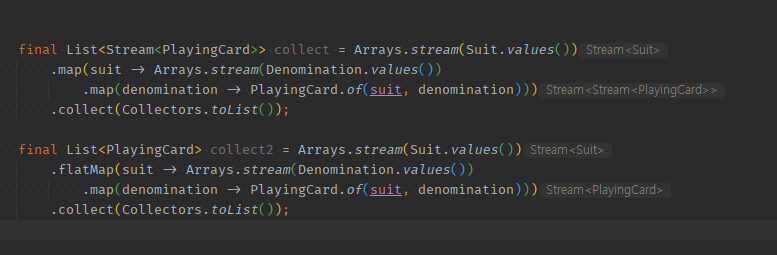
- 내부 Stream으로 바깥반복문Stream 입장에서 내부반복문or분신술에의한 Stream<>이 생겼다.
- 이 때, 바깥에서 flatMap()을 쳐주면, 내부 Stream을 바깥입장에서 동등하게 1개씩 보내줄 수 있다.
이중반복문 + 요소1,2를 재료로 새객체 생성 by .flatMap( .map() )
-
map( .map( -> 새객체 )) 이후 바깥쪽을
flatMap으로 고쳐주면,**Stream<Stream<>>에서 e1당 list2의 분신술들이 1개식 동등하게 넘어가도록 펴진다.**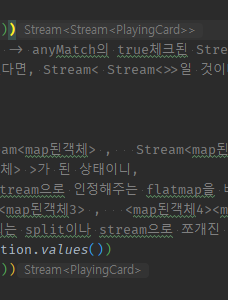
//2중 for문 + 생성자 -> e1, e2 1개씩 재료로 활용해서 새객체 모으기 // enum 2개가 반복문을 2번 돌 것임. Arrays.stream(Suit.values()) // 일단, e1이 결국엔 e2와 만나서 새로운 객체를 생성할 것이니 filter( e1->)이 아니라 map(e1->으로 시작한ㄷ) //.map(e1-> ) .map(e1 -> Arrays.stream(Denomination.values()) //e2도 결국엔 e1과 만나서 새로운 객체를 생성하니 map으로 시작한다. //.map(e2 ->) .map(e2 -> PlayingCard.of(e1, e2))) // 안쪽 stream은 collect를 하지 않고 -> anyMatch의 true체크된 Stream<Boolean?결과물> or map의 Stream<PlayingCard결과물>로서 Stream을 유지한다. // 안쪽stream의 안모으고 중간연산만 했다면, Stream< Stream<>>일 것이다. -> 바깥에서만 모은다면, 바깥만 list화되서 -> List<Stream<PlayingCard>> Type이 된다. .collect(Collectors.toList()); Arrays.stream(Suit.values()) //e1 vs list2들이 돌면서, Stream ( Stream<map된객체> , Stream<map된객체> , Stream<map된객체> )형태로 // -> 바깥 요소에 대해 Stream< Stream<객체> >가 된 상태이니, // -> 안쪽Stream()에 의한 분신술을 개별 Stream으로 인정해주는 flatmap을 바깥에서 적용한다. // --> Stream( <map된객체1><map된객체2><map된객체3> , <map된객체4><map된객체5><map된객체6> , <map된객체7><map된객체8><map된객체9> ] // 즉, flatmap은, [안쪽에서 분신술or반복되는 split이나 stream으로 쪼개진 것도 -> 바깥Stream에 1개씩 전달되도록 이정해주는 것] .flatMap(e1 -> Arrays.stream(Denomination.values()) .map(e2 -> PlayingCard.of(e1, e2))) .collect(Collectors.toList());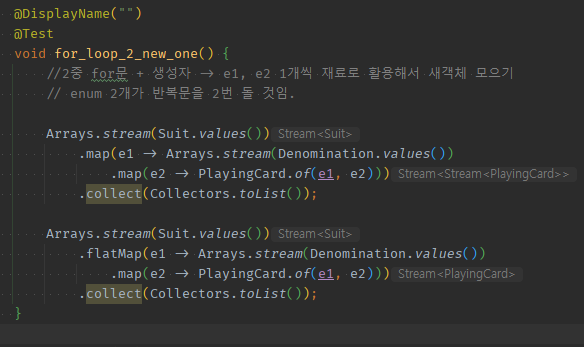
내부에서 분신술로 생긴 Stream<컬렉션<>> -> Stream.of()로 Stream<Stream<>>으로 만든 뒤 -> flatMap
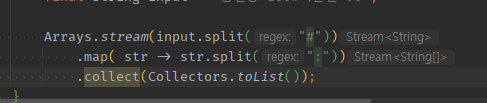
- split으로 분신술로 갯수가 늘어난 단일요소는
배열String[]들이 stream으로 넘어간다.
- 늘어난 분신술(배열)을
Stream.of()로 감싸면,Stream<String>들이 stream으로 넘어간다.
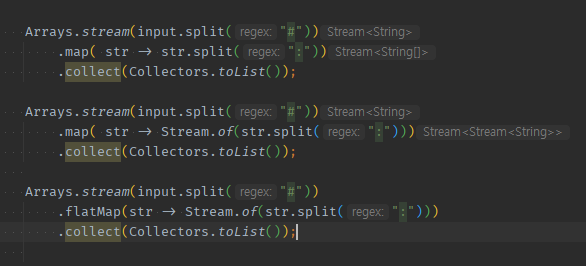
-
Stream.of(분신술)들을 map 대신 flatMap으로
변환후 뭉치면힌트가 사라진다.-
분신술들도 개별 1개씩이 순서대로 1개씩 넘어온다
-
-
java8이전
// 8버전 이전 // 2번 split해서, 이순신인 경우 그 점수를 출력 final String input = "홍길동:100#이순신:90"; final String[] splitInput = input.split("#"); for (final String nameAndScore : splitInput) { final String[] splitNameAndScore = nameAndScore.split(":"); final String name = splitNameAndScore[0]; final String score = splitNameAndScore[1]; if ("이순신".equals(name)) { System.out.println(score); } } -
stream
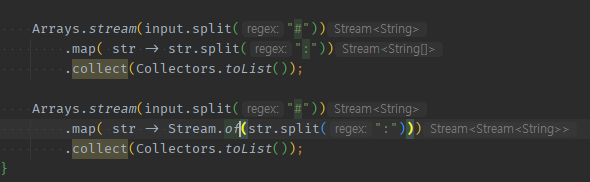
final String input = "홍길동:100#이순신:90"; Arrays.stream(input.split("#")) .map(str -> str.split(":")) .collect(Collectors.toList()); Arrays.stream(input.split("#")) // .map( -> 내부반복문or분신술) 로 Stream< String[] > 형태로 Stream < 배열/컬렉션 > 이 생겼다면, // -> Stream.of()로 쏴서, Stream< Stream< > > 형태로 만들어줘야 .map(str -> Stream.of(str.split(":"))) .collect(Collectors.toList()); Arrays.stream(input.split("#")) // flatMap()으로서, 내부 쪼개진 것들이 1개씩 보낼 수 있게 된다. // -> 즉, 안쪽에서 돌때 .stream()으로 도는게 아니라 split등 분신술을 썼다면, Stream.of()로 씌워줘야 바깥에서 flatMap을 맥일 수 있다. .flatMap(str -> Stream.of(str.split(":"))) .collect(Collectors.toList()); //홍길동 //100 //이순신 //90
외부List.of()를 배려한 가변인자(배열)의 내부처리는 stream보다는 List.of()
- 배열 ->
.stream()의 POSFIX completion ->.toList()를 해도 되지만 - 일괄처리 등 작업이 없다면 그냥 외부에서 쓰던
List.of( 가변배열 )을 그대로 쓰면 된다.
//배열 -> stream -> toList
public Cards(final Card... cards) {
this(Arrays.stream(cards)
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
//배열 -> List.of(밖에서 쓰던 것 그대로 내부에서 쓰기)
같은Type에 대해 일괄처리: List.of로 담아 + stream.일괄처리 —> Stream.of().일괄처리
-
개별 Card객체에 대해 일괄적으로 isAce인지 물어보고 싶다.
- 개별Card들을
List.of()의 컬렉션에 담고 ->stream(). 일괄처리
final boolean hasAce = List.of(first, second) .stream() .anyMatch(it -> it.isAce());- intellij추천
같은형이면 `Stream.of( , , )에 담아서 한번에 일괄처리
final boolean hasAce = Stream.of(first, second) .anyMatch(Card::isAce); - 개별Card들을
같은 도메인이라면 List.of()나 Stream.of()로 묶어서 메세지보내 일괄처리 or 내부변수 map변환 단순집계가 가능하며, 집계는 map + .getter()로 집계대상의 변수를 getter으로 변환하는 과정을 거쳐서 한다.
-
개별로 getter를 써서 일일히 다 더하는 경우
public static Object start(final Card first, final Card second) { final int sum = first.point() + second.point(); -
같은형이라
묶어서 -> 일괄처리or단순집계하는데, 내부 변수의 집계라면 getter로 변환해서 집계- 같은형을 묶을 땐,
List.of( , , )나Steram.of(, , , )
Stream.of(first, second) .mapToInt(it -> it.point()) .sum(); - 같은형을 묶을 땐,
일괄처리가 2번이상 등장한다면, 무조건 List.of(, , )로 묶어놓고 변수로 뽑아놓고 -> list.stream()으로 일괄처리 매번 적용한다.
public static Object start(final Card first,
final Card second) {
//1. 같은형의 [일괄처리/단순집계]가 2번이상 필요할 땐 -> 무조건 List.of()로 일단 묶어 변수로 뺀다.
final List<Card> cards = List.of(first, second);
// final int sum = Stream.of(first, second)
// 일괄처리1: 내부변수 단순집계
final int sum = cards.stream()
.mapToInt(it -> it.point())
.sum();
// final boolean hasAce = Stream.of(first, second)
// 일괄처리2: 일괄처리로 메세지보내기
final boolean hasAce = cards.stream()
.anyMatch(Card::isAce);
if (hasAce && sum == 11) {
return new Blackjack();
}
return new Hit();
}
반복문iter와 forEach
-
iterfor (CarDto currentCar : currentCars) { System.out.println(currentCar.getName() + " : " + collectDash(currentCar.getPosition())); } -
forEachcurrentCars.forEach(currentCar -> { System.out.println(currentCar.getName() + " : " + collectDash(currentCar.getPosition())); });
반복문fori 과 IntStream
-
foriStringBuilder track = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) { track.append("-"); } return track.toString(); -
IntstreamIntStream.range(0, position) .forEach(i -> { track.append("-"); }); return track.toString();
집계max( 숫자VO::compareTo )
-
값으로 변환한 뒤에.max()는 인자없이 바로 사용가능
this.cars.stream()
.mapToInt(car -> car.toInt())
.max()
.orElseThrow(() -> new NoSuchElementException("최대값이 존재하지 않습니다."));
-
값 객체끼리 비교는 필요조건이있다.
- 숫자VO에서 Comparable 구현클래스>
- VO로서 기본 equals 가지기
- compareTo 오버라이딩후 구현 -> Integer.compare( , )
- stream에서는
.max( 클래스::compareTo)로 비교하면서 집계
//1. Comparable<> impl하고
implements Comparable<$CLASS_NAME$>
//2. 오버라이딩 compareTo -> Integer.compare( this.숫변.toInt() , o(인자).숫변.toInt() );
return Integer.compare( this.$INT_VALUE$.toInt() , o.$INT_VALUE$.toInt());
//3. VO라면 값같으면 같은객체 보장용 -> equals && hashCode 오버라이딩
//4. stream에서는 .max집계( 클래스::compareTo )
cars.stream()
.max(Car::compareTo)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException());
참고) 제네릭메서드 + reduce로 max 집계
private static <T extends Comparable<T>> T max(final List<T> list) {
return list.stream()
.reduce((a, b) -> a.compareTo(b) > 0 ? a : b)
.get();
}
list필터링- filter ( -> 객체. t/f반환메서드 사용 )
- 조건에 부합하는 것만 골라내야한면,
filter+객체에게 시켜서 t/f반환하도록 한다.
this.cars.stream()
.filter(car -> car.isSamePosition(maxPosition)) // 필터로 조건메소드 참인 것만 골라내기
.collect(Collectors.toList());
특정 문자열속성 joinning - (map+getString -> joining)
cars.stream()
.map(car->car.getName())
.collect(Collectors.joining(System.lineSeparator()));
만족하는 총 갯수 카운팅(for+if+add ->) by filter.() + (다모아서) count()
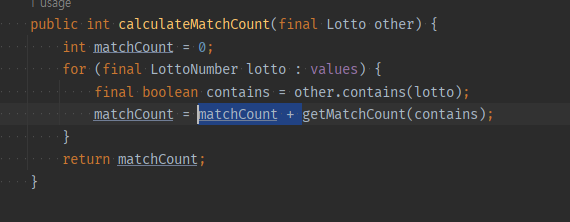
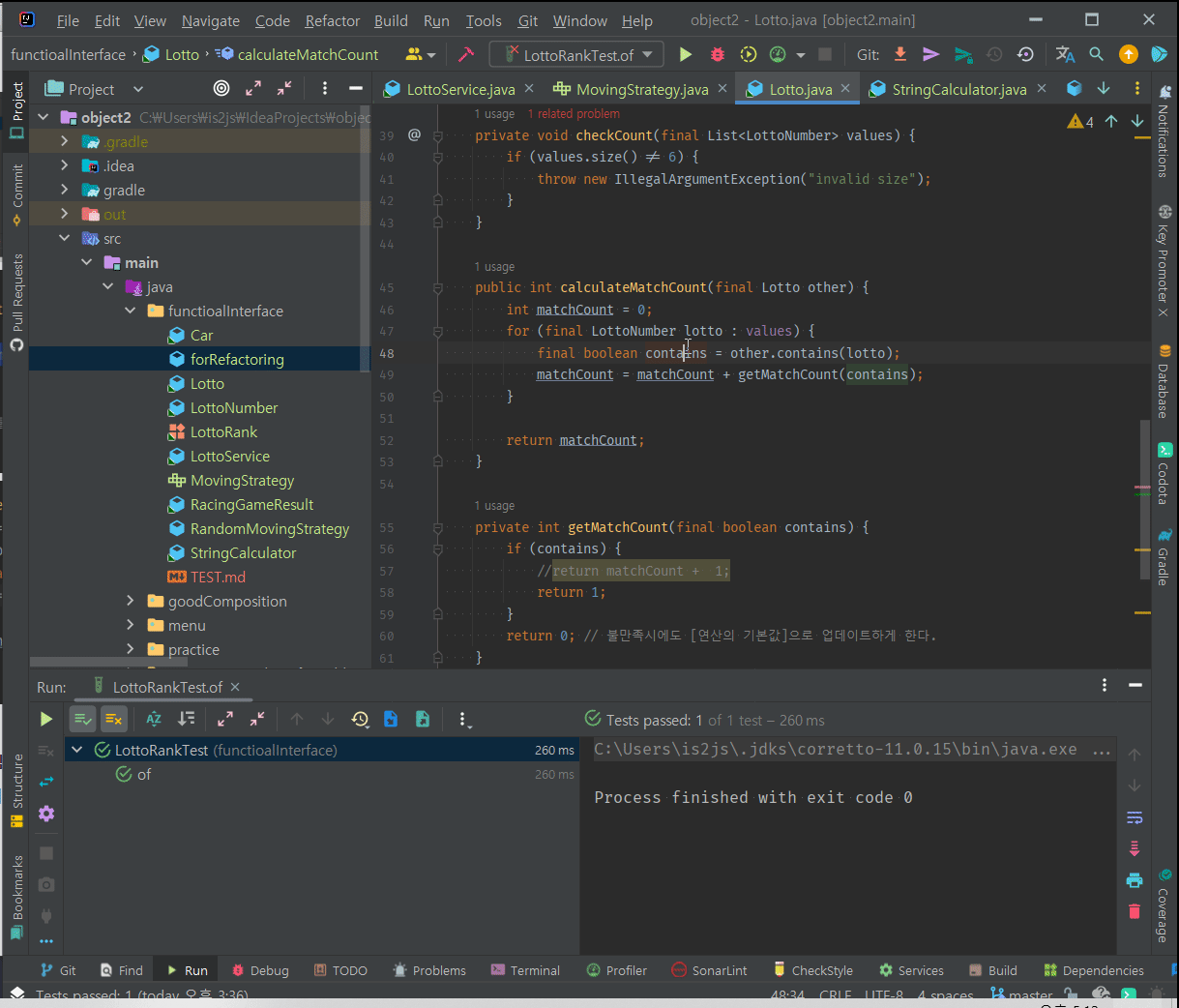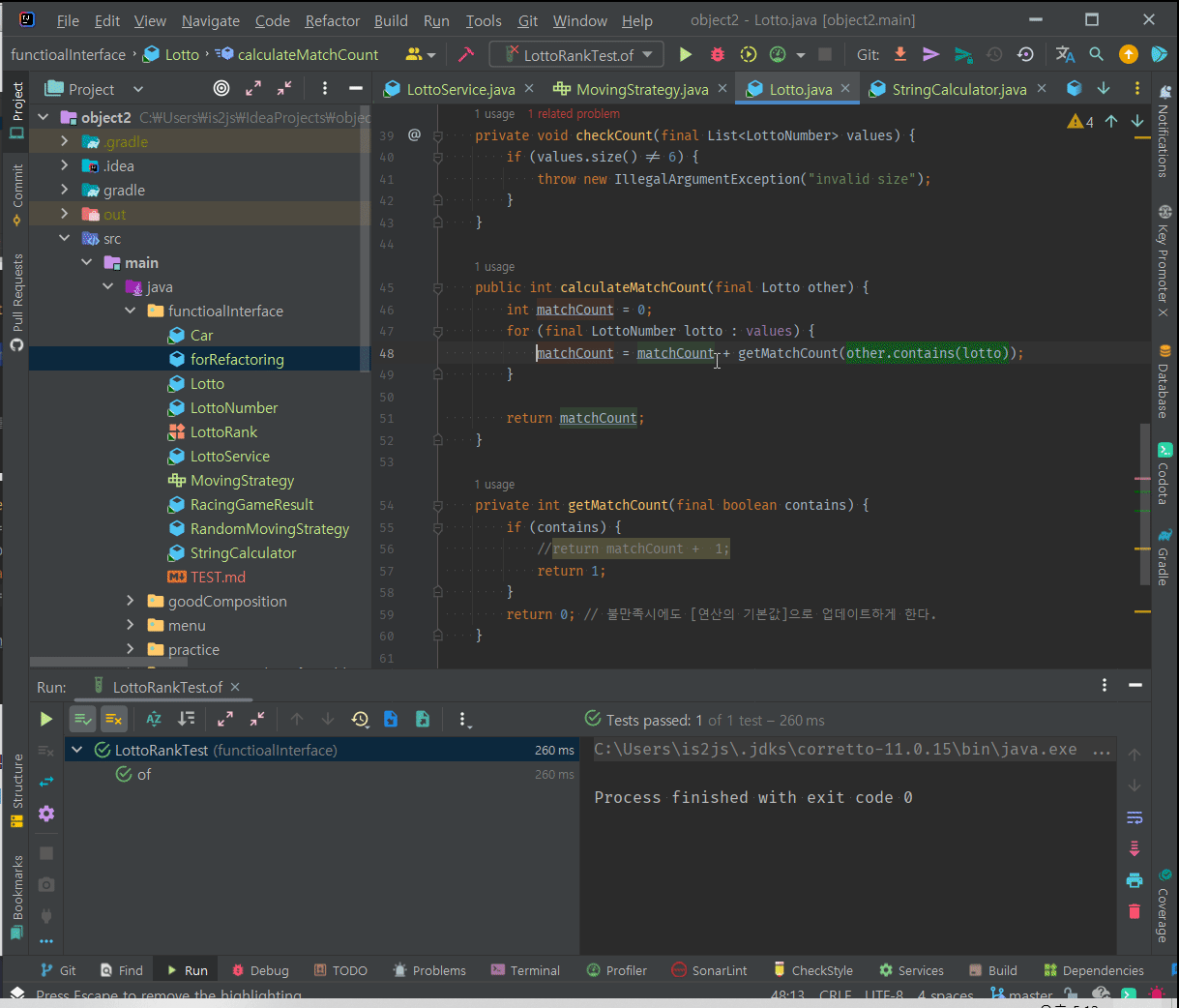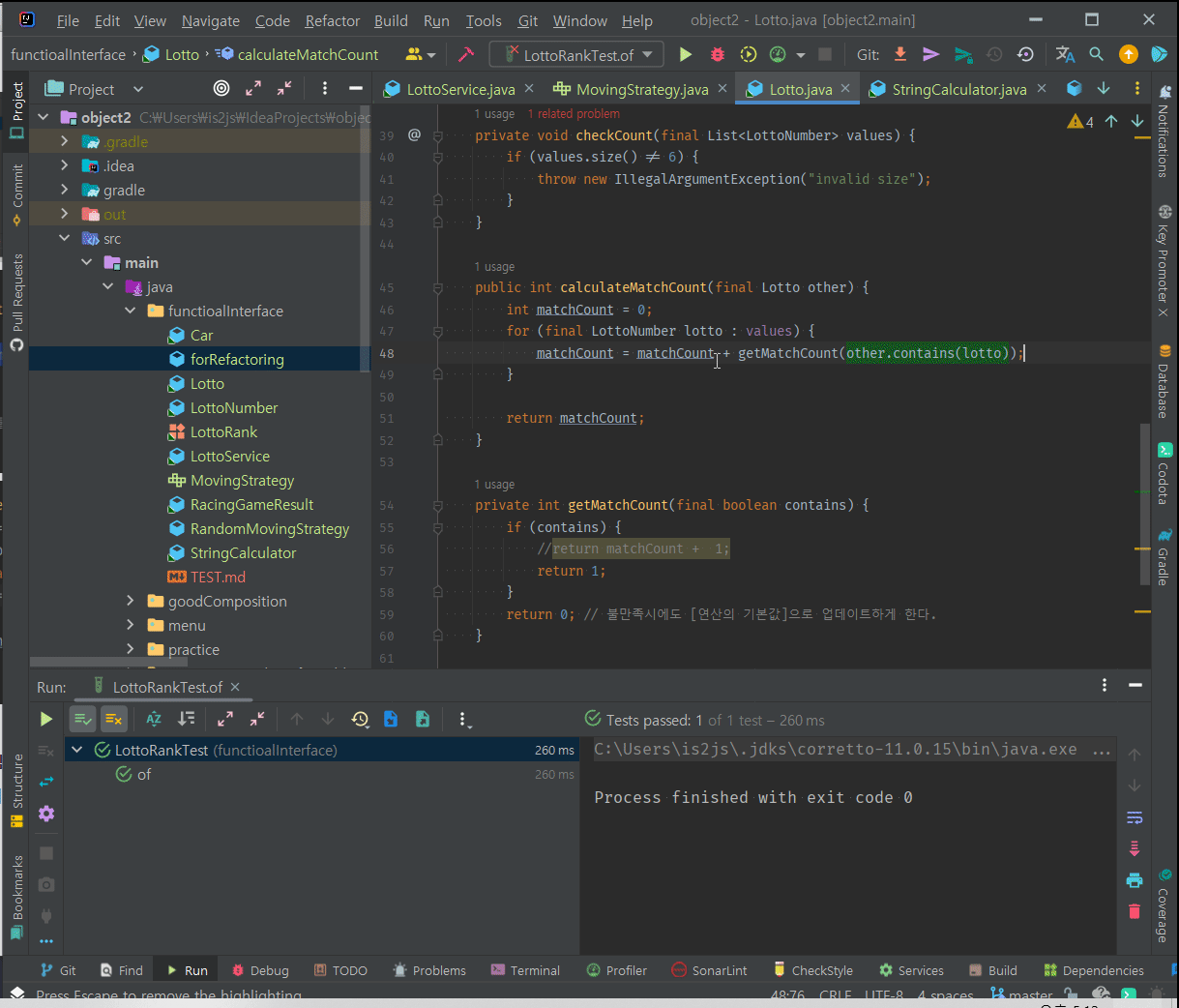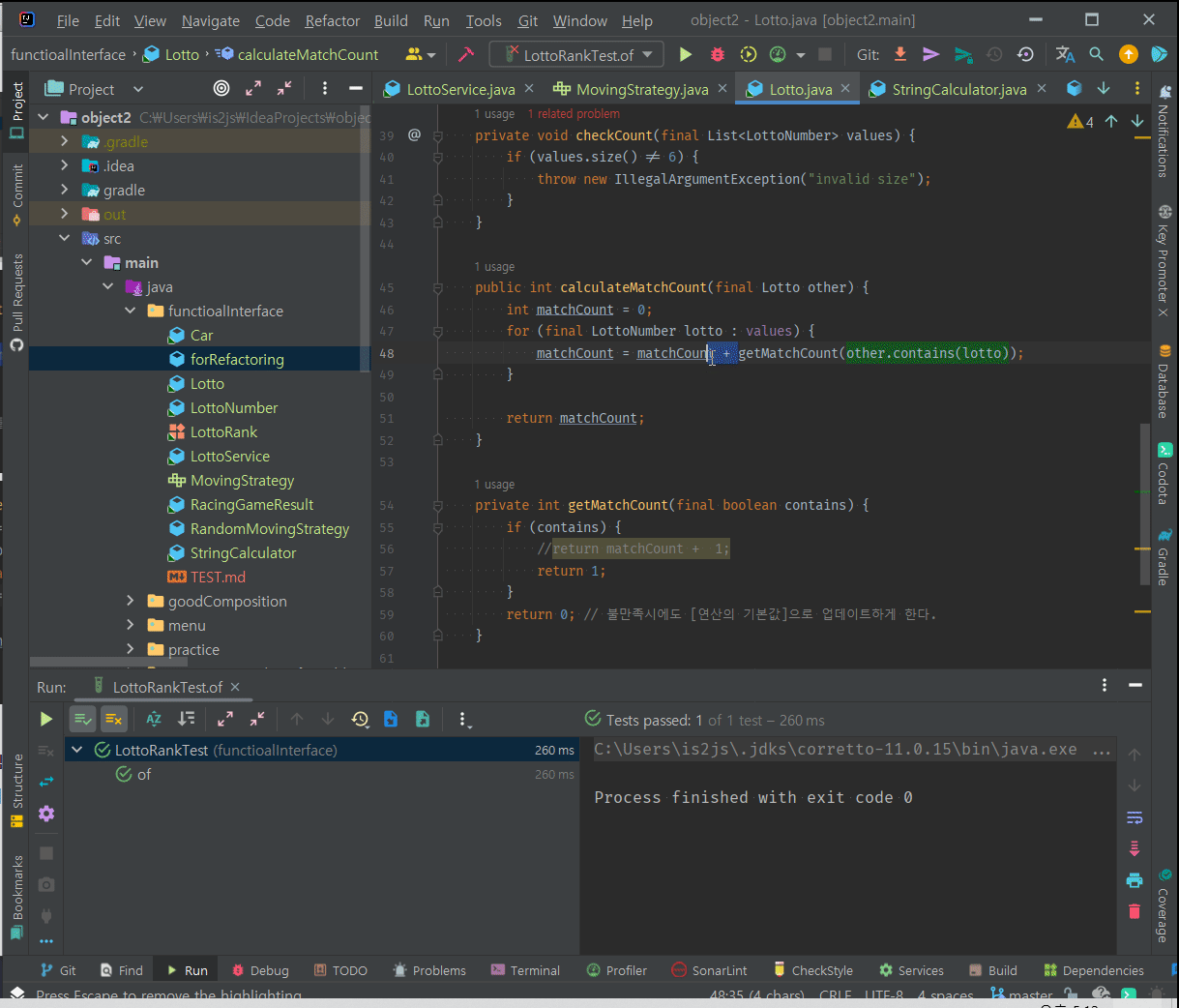
public int match(final Lotto other) {
return (int) other.value.stream()
.filter(it -> contains(it))
.count();
}
public boolean contains(final LottoNumber number) {
return value.contains(number);
}
}
private int calculateAceCount() {
return (int) playingCards.stream()
.filter(PlayingCard::isAce)
.count();
}
역순 list
List<Rank> ranks = Arrays.asList(Rank.values());
Collections.reverse(ranks);
역순 stream With comparable 상속
.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder())
누적은 mapToType + .집계 » .reduce(초기값, 해당Type::집계함수) 더 깔끔
//수정전
return rankResults.entrySet().stream().map(Entry::getValue).reduce(0, Integer::sum)
* Lotto.LOTTO_PURCHASE_MONEY;
//수정후
return rankResults.entrySet().stream()
.mapToInt(Entry::getValue)
.sum() * Lotto.LOTTO_PURCHASE_MONEY;
toSet() / toMap() 등… 다른 것으로도 가능
- set
numbers.stream() // 스트림을 열고
.map(Number::new) // 가공하여
.collect(Collectors.toSet()); // 결과를 셋으로 만든다.
- map
LOTTO_NUMBER_CACHE = IntStream.rangeClosed(MIN_LOTTO_NUMBER, MAX_LOTTO_NUMBER)
.boxed()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
number -> number, //Function.identity()
LottoNumber::new
));
- map을
자기자신을 key, 0을 상수 value으로 초기화해서 생성- it -> it :
Function.identity()로 자기자신 그대로 반환 이용가능하나보다 - it -> 0 : 숫자는 1단어로 바로 안되나보다.
- it -> it :
private Map<Rank, Integer> emptyRankMap() {
return Stream.of(Rank.values())
.collect(toMap(Function.identity(), r -> 0));
}
-
map을
자기자신을 key+key별(그룹별)로 누적return lottos.getLottos() .stream() .map(winningLotto::getRankByLotto) .collect(groupingBy(identity(), () -> new EnumMap<>(Rank.class), summarizingLong(Rank::getPrize))); -
toMap으로 다른type의 맵을 만드려면 3, 4번째 인자 동시에 추가해줘야한다.
public static Map<Player, Integer> from2(final Players players) { return players.getGamblers() .stream() .collect(Collectors.toMap( Function.identity(), gambler -> caculateProfit(players, gambler), (x, y) -> y, // 3번재에는.. 올드,뉴 중에 뉴를 선택?? 머지? LinkedHashMap::new) // 4번째에.. 만들 타입 ); }
contains와 anyMatch or noneMatch & equals(같은게 & 하나라도 있냐)
-
객체 속 특정필드에 대한contains(boolean) -> stream +map(필드)+anyMatch & equals-
객체 속 필드가 아니라 객체list contains 객체라면
- stream + anyMatch & equals(하나라도 같은게 있냐)
private boolean containsSection(Section section) { return sections.stream() .anyMatch(value -> value.equals(section)); } -
stream을 안쓴다면
- 빈list add getter로
필드list->contains ( 객체.getter )
- 빈list add getter로
-
stream을 쓴다면
-
map으로 필드list로 변환 -> 같은게 하나라도 있나anyMatch + equals
-
-
! contains라면-
map으로 필드list로 변환 -> 하나라도 같은게 없어야noneMatch + equals
private boolean isFirstSection(final Section section) { return value.stream() .map(Section::getDownStationId) .noneMatch(downStationId -> section.getUpStationId().equals(downStationId)); // return !getDownStationIds().contains(section.getUpStationId()); } /* private List<Long> getDownStationIds() { return value.stream() .map(Section::getDownStationId) .collect(Collectors.toList()); }*/ -
-
중복검사도 contains와 같다. 같은게(equals) 하나라도 있냐(anyMatch)
-
같은게 있으면 예외를 던지는데, ifPresent()는 예외던지는 용이 아니니 조심하자
-
잘못된 예
private void validateDuplicateSection(final Section section) { values.stream() .filter(value -> value.isSameSection(section)) .findAny() .ifPresent(value -> { throw new SectionCreateException(SECTION_ALREADY_EXIST_MESSAGE); }); } -
anyMatch를 boolean으로 받아서 if문에 걸어 처리
private void validateDuplicateSection(final Section section) { boolean exist = values.stream() .anyMatch(value -> value.isSameSection(section)); if (exist) { throw new SectionCreateException(SECTION_NOT_CONNECT_MESSAGE); } }
-
특정로직에 해당하는 것이 없느냐도 contains와 같다. 해당하는 게(compareMethod) 하나도 없나(noneMatch)
- 비교메서드는 poisitive하게 작성하고 -> 하나도 없느냐의 부정어를 noneMatch로 한다
private void validateSectionConnect(final Section section) {
boolean isNotConnected = values.stream()
.noneMatch(value -> value.haveStation(section));
if (isNotConnected) {
throw new SectionCreateException(SECTION_NOT_CONNECT_MESSAGE);
}
}
해당(포함)하는게 있으면 -> 찾아서 -> 특정 로직 수행까지 진행된다면, anyMatch + 비교메서드가 아니라 filter + findAny 찾아놓고 -> ifPresent( -> 수행메서드() )로 다르게 작성한다.
-
해당하는게 있느냐만 물어보고 끝난다(예외 던지기, 조건문용)면-
anyMatch/noneMatch->비교메서드/equals
-
-
해당하는게 있으면 -> (찾아서) -> 수행해라면-
filter & 비교메서드/equals+findAny()+ifPresent( -> 수행메서드())
private void cutInSection(final Section section) { values.stream() .filter(value -> value.isSameUpStation(section.getUpStation()) || value.isSameDownStation(section.getDownStation())) .findAny() .ifPresent(foundSection -> updateCutInSection(section, foundSection)); } -
로또
shuffle후 subList -> .limit(6)으로 를 통한 랜덤추출 구현
public static Lotto issueLotto() {
Collections.shuffle(LOTTO_NUMBERS);
return new Lotto(LOTTO_NUMBERS.stream()
.limit(6)
.sorted()
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
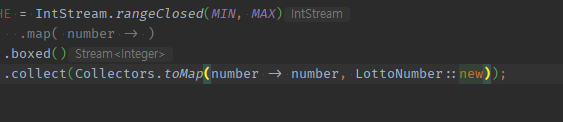
IntStream + boxed(Integer for Map 제네릭) toMap( it -> key, value)으로 <숫자, 숫자VO>매핑 Map 만들기
-
.map() 없이
-
.boxed()수동 필수 -
toMap( -> a, b)의 2번째 Value 자리에 생성자호출 -> 메서드파라미터 필수!
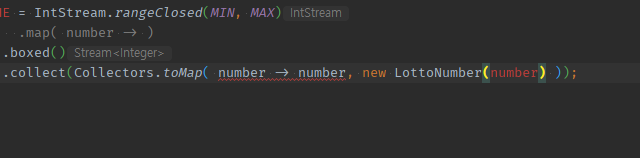
public synchronized static LottoNumber valueOf(final int number) {
checkNumberRightRange(number);
if (LOTTO_NUMBER_CACHE == null) {
LOTTO_NUMBER_CACHE = IntStream.rangeClosed(MIN_LOTTO_NUMBER, MAX_LOTTO_NUMBER)
.boxed()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(lottoNumber -> lottoNumber, LottoNumber::new));
}
return LOTTO_NUMBER_CACHE.get(number);
}
가변 변수 제거 -> 아직 list가 아닌 [stream상태로 모아서] -> map변환 못한 경우 -> 모아서 list만들면서 map collectAndThen( toList(), 변환메서드)
- stream + stream -> concat 하여 map할 기회를 놓친 체
.collect( toList())하여 이후 또 개별 stream + map해줘야한다? -> 바로 할 수 있다.- 2stream 을 1개 list로 변환해서 모으고 -> 포장까지 할 수 있다.!!
- 기존list.stream() + 새list.stream() -> Stream.concat() -> collect(
collectingAndThen( toList(), 포장생성자::new )
public Lottoes combine(Lottoes other) {
List<Lotto> result = new ArrayList<>();
result.addAll(lottoes);
result.addAll(other.lottoes);
return new Lottoes(result);
}
// 변환후
public Lottoes combine(Lottoes other) {
return Stream.concat(lottoes.stream(), other.lottoes.stream())
.collect(collectingAndThen(toList(), Lottoes::new));
}
블랙잭
for for 객체 생성 -> stream map -> stream map -> 앞에 map을 flatmap -> toCollection( 모은 결과물stream -> new 원하는 컬렉션 생성)
-
앞에 것 suit 1개당-> 여러 denomination.values()들이여러개의 결과물을 만들 것이다. 앞에 것들suit_1 + suit_2 + … ->각각에 해당하는 결과물들을.flatmap()으로다 모은다- 모아진 stream을
toCollection( -> )로 또 원하는 컬렉션(Stack)으로 변경생성
Stack<PlayingCard> playingCards = Arrays.stream(Suit.values())
//.map(suit -> Arrays.stream(Denomination.values())
.flatMap(suit -> Arrays.stream(Denomination.values())
.map(denomination -> PlayingCard.of(suit, denomination)))
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(Stack::new));
Collections.shuffle(playingCards);
this.playingCards = playingCards;
Count Map 생성
CountMap01 EnumMap -> 결과list를 [ 직접 0 초기화후 map.put카운팅]
- 제한된 key값들을 도는 Enum.values().stream + forEach put( , 0) + 결과List돌면서 개별 +1
private final EnumMap<Rank, Integer> result = new EnumMap<>(Rank.class);
// 카운트 0으로 초기화
{
Arrays.stream(Rank.values()).forEach(rank -> result.put(rank, 0));
}
// 단일key를 돌면서
result.put(rankPrize, result.getOrDefault(rankPrize, 0) + 1);
[추천] CountMap02 EnumMap -> 결과list를 [초기화없이 map.merge]
- 미리 0 초기화 없이
알아서 직전value(없으면 0부터) 누적해주는 ->map.merge( 객체key, 누적해넣을값, Integer.sum()으로 기존value와 누적방법 Bifunction )
result.merge(rank, 1, (before, after) -> Integer.sum(before, after))
final List<Rank> results = lottos.stream()
.map(lotto -> match(lotto, winningLotto))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
final EnumMap<Rank, Integer> result = new EnumMap<>(Rank.class);
results
.forEach(rank -> result.merge(rank, 1, (before, after) -> Integer.sum(before, after)));
private Result(final LottoGroup lottos, final WinningLotto winningLotto) {
for (Lotto lotto : lottos.get()) {
Rank rank = Rank.of(lotto.countSameNum(winningLotto), lotto.contains(winningLotto.getBonusNumber()));
value.merge(rank, 1, Integer::sum);
}
}
[추천] CountMap03 -> 일급vs단일 [key처리와 초기화없이 counting을 동시에 ] by Collectors.groupingBy
- 일급vs단일의 결과값list 바로 뽑은 뒤 처리하는 대신
처리 + counting을 동시에->- groupingBy(단일vs단일로 객체key로직, summingInt( count -> 1))으로 한번에 로직처리 + Map만들기
this.value = lottos.stream() // 일급vs단일 -> 단일vs단일 -> 결과 List
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
lotto -> match(lotto, winningLotto), // 단일vs단일로 결과객체 1개
Collectors.summingInt(count -> 1))); // 없으면 0부터 1씩 count누적시킴
맵 타입 지정 가능
final EnumMap<GameResult, Integer> dealerResult = gamblers.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
gambler -> getResultPlayer(dealer, gamblerResult, gambler),
() -> new EnumMap<>(GameResult.class), // Map타입 가운데서 지정
Collectors.summingInt(count -> 1)
));
map 돌아서 처리하기
key만 == 1개만 필요한 경우 : map.keySet().stream().map() -> map.get(key)
- key객체만 돌기 때문에 -> map(value)을 내부에서 따로 호출(map.get(
도는 key)해야한다.- key가 getter를 소지한 객체인 경우,
객체key 자체의 값과 map에 박혀있던key의 값을 처리할 수 있다.
- key가 getter를 소지한 객체인 경우,
public long getPrize() {
long prize = 0;
for (Rank rank : value.keySet()) {
prize += (long) rank.getPrize() * value.get(rank);
}
return prize;
}
value만 == 1개만 필요한 경우 : map.values().stream().map() -> map.get(key)
private static long getTotalReturnByLottoResult(Map<Rank, LongSummaryStatistics> lottoResult) {
return lottoResult.values()
.stream()
.mapToLong(LongSummaryStatistics::getSum)
.sum();
}
key+value가 둘다 필요한 경우: map.entrySet().stream().map() -> it.getKey + it.getValue
- stream상 1개 값이 key, value를 다 가지고 있으며,
map을 따로 호출할 필요 없이 뽑아서 쓰면 된다.- cf) Long타입의 누적은
.reduce( 0L로 시작하고, 집계함수자리에는Long::xxx)를 넣어주면 된다.
- cf) Long타입의 누적은
private Long calculateTotalReward() {
return rankResults.entrySet()
.stream()
.map(result -> Rank.calculateMoney(result.getKey(), result.getValue()))
.reduce(0L, Long::sum);
}
mapToType한 뒤, 정해진 .집계메서드()쓰는게 젤 편하다. 어느 방식이든 default값은 0으로 쳐준다.
//요렇게도 사용할 수 있을 것 같네요🙂
public double getRateOfProfit(Money money) {
long totalMoney = result.entrySet()
.stream()
.mapToLong(entry -> entry.getKey().multiply(entry.getValue()))
.sum();
return money.getRateOfProfit(totalMoney);
}
map을 돌며, 누적하기
int (mapToInt -> sum() )
value.entrySet()
.stream()
.mapToInt(Entry::getValue)
.sum() * Lotto.LOTTO_PURCHASE_MONEY;
long with Enum ( map -> reduce( 0L , ) )
rankResults.entrySet()
.stream()
.map(result -> Rank.calculateMoney(result.getKey(), result.getValue()))
.reduce(0L, Long::sum);
//Rank
public static long calculateMoney(final Rank currentRank, final long count) {
return currentRank.reward * count;
}
누적 계산( int vs Long )
[추천] 누적 연산이 미리 정해진 계산: mapToType( -> ) -> .sum()
-
최종결과가
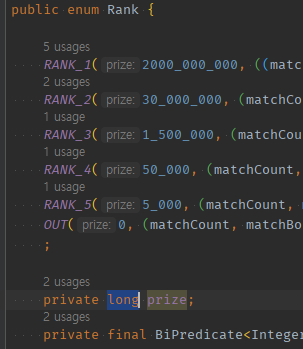
21억이 넘냐 안넘냐에 따라서 애초에 자료형을long으로 선언한다.public enum Rank { FIRST(2_000_000_000, 6), SECOND(30_000_000, 5), THIRD(1_500_000, 5), FOURTH(50_000, 4), FIFTH(5_000, 3), NOT_THING(0, 0), ; private final long reward; private final int hitCounts;-
나는 단일 값이 21억이 안넘어서 default int로 선언했지만, 누적합에서 21억 넘을 수 있으니 미리 자료형을
long으로 해주자-
내가 최종결과 간과 한 것
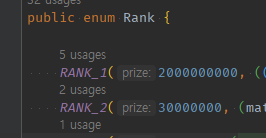
-
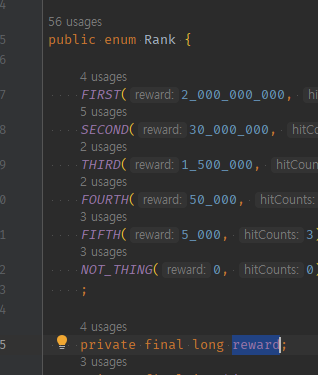
최종결과가 21억이 넘을 가능성 -> 미리 long타입으로 선언해준 경우
-
참고) long타입 표기를 위해
L붙일 경우_끊음 표시 못넣는다.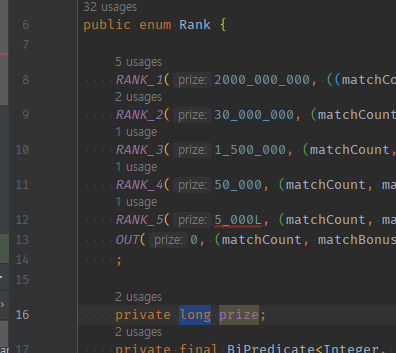
-
-
메서드 returntype도 long으로 자동으로 된다.
public long getPrize(final Integer count) { return this.prize * count; } -
계산도 default값 생각하지말고 누적계산을 정해진
.sum()로 시키면 된다.public long getPrize() { return value.entrySet() .stream() .filter(result -> !result.equals(Rank.OUT)) .mapToLong(it -> it.getKey().getPrize(it.getValue())) .sum(); //.reduce(0, Integer::sum); }
-
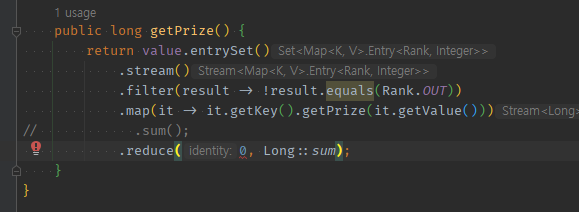
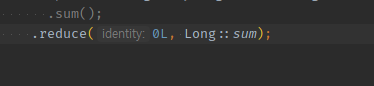
누적 연산을 커스텀으로 할 경우, map( -> ) .reduce( default값 , Long::sum) -> 불편
-
변환되는 타입이 표기는 안되지만, type이 맞지 않는 경우, 알아서
누적연산 메서드 자리에서 에러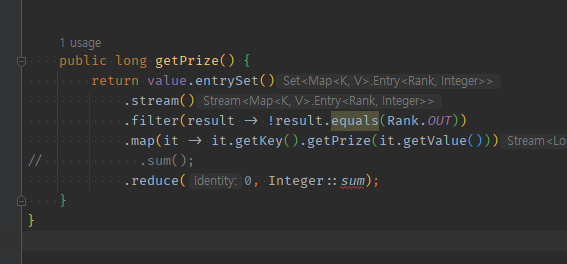
[비추] for 누적 + 매번 long 형변환하여 +=누적
- 그냥 자료형 자체를 1개를 long으로 선언했어도 됨.
public long getPrize() {
long prize = 0;
for (Rank rank : value.keySet()) {
prize += (long) rank.getPrize() * value.get(rank);
}
return prize;
}
로또
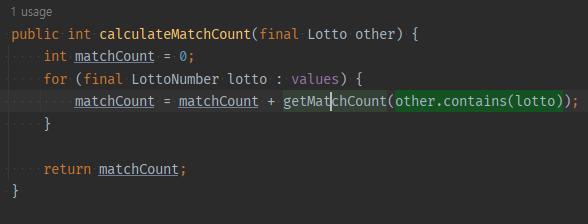
[누적될 값을 반환하는 메서드]를 받아 가변변수 누적을 stream + map + sum으로 누적하기
-
외적으로 가변변수의 누적은 스트림으로 대체할 수 있다.
-
일단 누적될 로직은 리팩토링해서 1개의 메서드로 모은다.
-
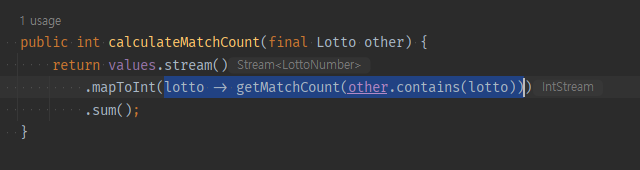
stream으로 가변변수에 값을 누적한다면
- 원시값 누적이면 .reduce(0 , 연산람다식 )
- 변환된 값 누적이면, mapToXXX( ) -> .sum()을 때리면 된다.
-
체스
enum에서 filter(해당문자열 확인) + orElseThrow로 enum.of( input ) 검증포함해서 찾기
문자열로 확인시 정규식(다 equals인데 하나만 startsWith -> 정규식 비교로 통일) 이 필요하면 그것으로 filter
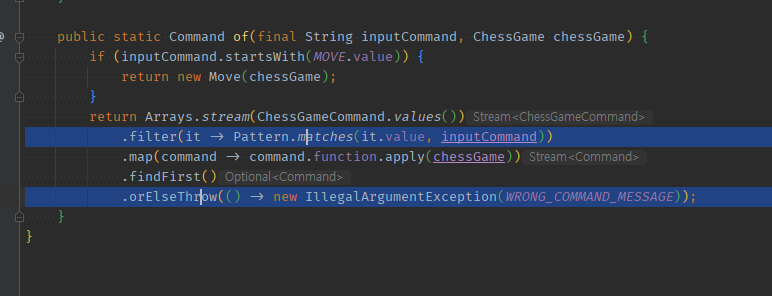
public static Command of(final String inputCommand, ChessGame chessGame) {
// web등으로 갈 것 같으면, inputView대신 빈값 null검사를 여기로
// if (inputCommand.startsWith(MOVE.value)) {
// return new Move(chessGame);
// }
return Arrays.stream(ChessGameCommand.values())
// .filter(it -> it.value.equals(inputCommand))
.filter(it -> Pattern.matches(it.value, inputCommand))
.map(command -> command.function.apply(chessGame))
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException(WRONG_COMMAND_MESSAGE));
}
일반 오리
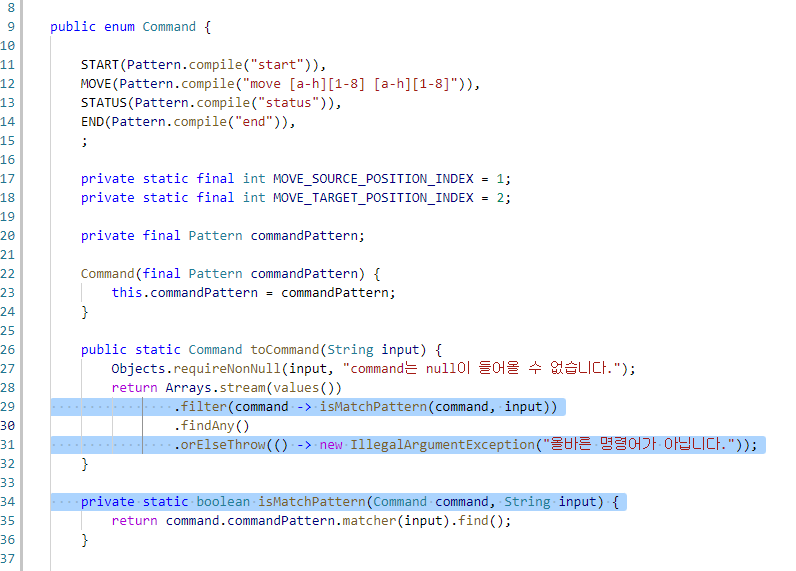
public enum Command {
START(Pattern.compile("start")),
MOVE(Pattern.compile("move [a-h][1-8] [a-h][1-8]")),
STATUS(Pattern.compile("status")),
END(Pattern.compile("end")),
;
Command(final Pattern commandPattern) {
this.commandPattern = commandPattern;
}
public static Command toCommand(String input) {
Objects.requireNonNull(input, "command는 null이 들어올 수 없습니다.");
return Arrays.stream(values())
.filter(command -> isMatchPattern(command, input))
.findAny()
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("올바른 명령어가 아닙니다."));
}
private static boolean isMatchPattern(Command command, String input) {
return command.commandPattern.matcher(input).find();
}
문자열 split된 것을 skip으로 처리
-
없었다면, 개별 substring했어야함
public static Positions from(final String command) { return new Positions(Arrays.stream(command.split(SPLIT_DELIMITER)) .skip(1) // [move a2 a4]에서 -> [a2, a4]만 추출 .map(Position::from) .collect(Collectors.toList())); }
noneMatch/ allMatch -> (다모았는데) 특정조건은 하나도 없어야한다 / (다모았는데) 모두 만족해야한다. or [배반조건으로서 둘중에 한쪽만] 특정조건만 존재해야한다.
// king들을 다 모았는데, 특정조건 (black인놈은) 하나도 없어야한다
public boolean hasBlackKingCaptured() {
return collectKing().stream()
.noneMatch(Piece::isBlack);
}
// king들을 다 모았는데, white는 없어야한다 -> 둘중에 black만 존재해야한다
public boolean hasWhiteKingCaptured() {
return collectKing().stream()
.allMatch(Piece::isBlack);
}
지하철 경로
groupingBy로 일급컬렉션을 하위 객체 필드로 가지는 도메인의 findAll() 처리하기
-
상황
-
Line 도메인에 response용 하위 도메인 Sections를 sql join으로 붙일 경우
-
단건 조회(findById)임에도, Line(pk) <—left join— Section(fk)시 line에 대해서는 1xm개의 데이터가 생긴다.
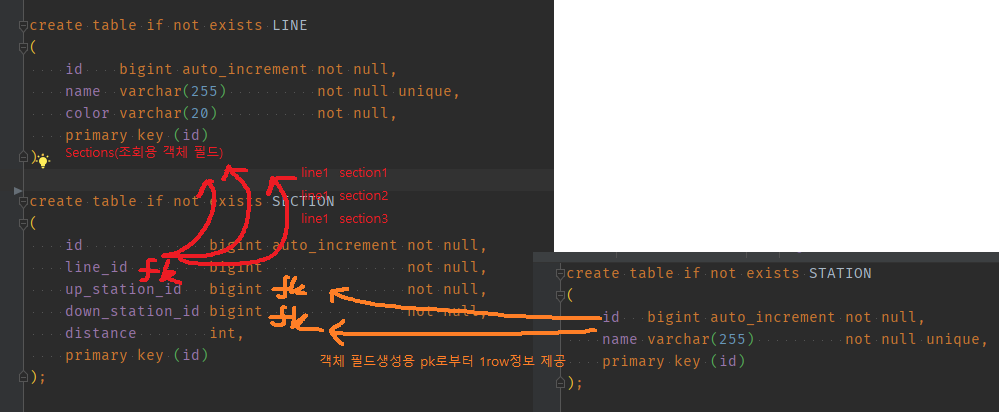
-
-
해결
-
sql join으로 line의 단건 조회
findById의 select절에 section정보를 붙여넣는다.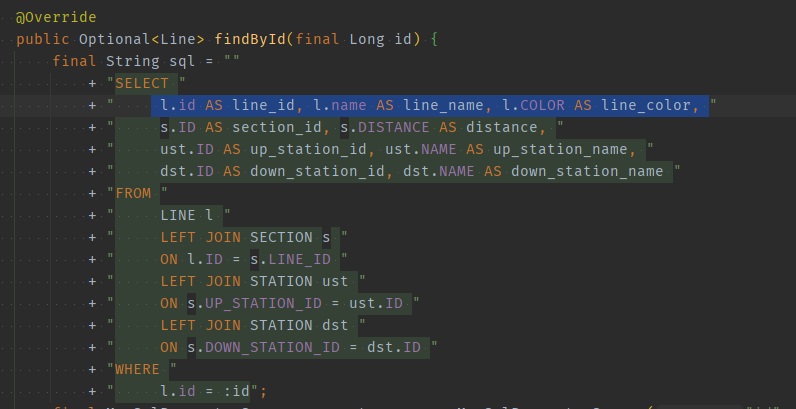
-
queryForList를 통해 단건 조회임에도 여러개 생기는 rows들을 Map으로 반환받고 난 뒤
-