while 분기속 if break; 리팩토링
반복문 속에서 if 종료조건 break;을 처리하기
📜 제목으로 보기
- while(true) if break; 로 먼저 작성하기
- while(true) 반복문 속 if break;의 메서드 추출
- 01 if 종료조건 break; 는 메서드 추출을 위해 -> if 종료조건 flag변수(Enum) Off처리; + continue;로 while조건문으로 보낸 뒤 -> while조건문에 flag검사( not isOff()? )로 변경한다.
- 02 flag .off() 처리후 continue;로 올라간 조건문 검사를 while (true) -> 플래그변수가.isOff()인지 검사로 변경한다.
- 03 if break; -> if flagOff + contine + while flag isOff()검사 해줬어도 if조건식에 extract method는 depth를 못 줄인다
- 04 if조건문의 메서드추출은 수동으로 통째로
- 05 복붙으로 코드 옮겨가고 flag변수.Off() 처리후 continue; 대신 -> 1) early return; + 2) 추출메서드를 while문 맨 뒤에 배치하여 flag처리 직후 while조건문 검사하는 continue;효과내기
- while문을 재귀로 고치기
- 01 while속 돌아가는 모든 (분기)로직들을 통으로 1개 메서드로 추출
- 02 while !EndFlag 조건문 = flag 확인문 -> 재귀 속 break(EndFlag)하는 종착역으로서 먼저 if early return로 정의해주기
- 03 반복되던 로직의 if return종착역까지 완성됬으면 -> 함수 끝날 때 자신(메서드) 부르기
- 04 while to 재귀로 만든 이유 -> inputView가 포함된&&입력받는 것부터 시작하는 로직은 try로 살펴보는 시작이 input부터이면서 && catch시 다시 input부터 시작하도록 재귀함수형태를 만들어하므로
- Enum과 명령어 문자열 캡슐화 + 외부input시 검증까지
- 외부input으로 찾는 Enum의 filter에 정규식을 쓰면?
- enum으로 분기 제거까지 적용하려면?
while(true) if break; 로 먼저 작성하기
01 while(ture)의 무한반복문에서 break;분기부터 작성해보기
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
// 0. input객체 + 메인로직 특정객체 미리 만들어두기
final InputView inputView = new InputView();
final 특정객체 특정객체 = new 특정객체();
// 1. 일단 while(true) {} 로 돌아가면서 break부터 생각해본다.
while (true) {
// 1-1. 매번 받는 입력도 돌아가야한다.
final String inputCommand = inputView.inputCommand();
// 1-2. 가장 간단한 경우부터 생각해본다. 어차피 if break; if continue; 일듯 싶어서
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
}
}
private static class 특정객체 {
}
}
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final InputView inputView = new InputView();
final 특정객체 특정객체 = new 특정객체();
while (true) {
final String inputCommand = inputView.inputCommand();
// 1-3. if 종료버튼 + if 특정객체 종료조건 까지 걸려서 멈춘다고 한다.
// -> end를 눌럿을 때, ready / running / finished 중 finished 상태만 -> 로직종료 + 입력도 종료(break;)
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
if (특정객체.isNotRunning()) {
break;
}
}
}
}
private static class 특정객체 {
public boolean isNotRunning() {
return true;
}
}
}
02 break;를 가진 분기를 만들었다면, 편하게 나머지 분기들을 늘려도 된다. 대신, if 속 break;는 flag로 밖에 처리 못하니, while문 맨 끝에 배치하고, 위로 채워가자?!
여기선, if 종료버튼 눌른 뒤, if 특정조건 아니면 break;종료를 안한다. (게임 결과 출력은 Finished상태가 아니라, RunningToFinished되는 game.end()호출 순간이다.)
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final InputView inputView = new InputView();
final 특정객체 특정객체 = new 특정객체();
while (true) {
final String inputCommand = inputView.inputCommand();
// 1-3. if에 if 특정객체에 조건 까지 걸려서 멈춘다고 한다.
// -> end를 눌럿을 때, ready / running / finished 중 finished 상태만 -> 로직종료 + 입력도 종료(break;)
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
// 1-4-1. end눌렀을 때 상태3개 중 ready/running/finished , 바로 finished 상태면 바로 종료?? ready -> 바로 종료
if (특정객체.isNotRunning()) {
break;
}
//1-4-2. break;로 바로 종료(ready/finished)의 배반인 running 상태
// -> if early return처럼 early break 아래부분도 [if의 배반]이다.
// -> end 눌렀는데 아직 특정객체가 Running 중 이라면?
// (1) running중인 정보(board)를 가지고 finished상태로 만들도록 명령한 뒤
특정객체.end();
// (2) 이 때만(ready(X), finsihed(X) running to finished by .end() )시에만 게임결과를 출력한다.
// my) running -> finished 순간을 캐취해서 게임결과를 출력해줘야한다. (가만히 있는 finished는 출력할 필요도 없이 종료)
System.out.println("게임 하다가 끝났기 때문에, 게임 결과를 출력합니다.");
}
}
}
private static class 특정객체 {
private String state;
public 특정객체() {
this.state = "running";
}
public boolean isNotRunning() {
if (this.state.equals("running")) {
System.out.println("running상태입니다.");
return false;
}
System.out.println("ready or finished상태입니다.");
return true; // ready나 finished상태
}
public void end() {
System.out.println("상태가 running -> finished");
this.state = "finished";
}
}
}
state패턴으로서 start명령어가 있다면, ready가 기본이 된다. (end만 있을 땐 running을 기본으로 해서 게임->종료되는 상황 연출)
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final InputView inputView = new InputView();
final 특정객체 특정객체 = new 특정객체();
while (true) {
final String inputCommand = inputView.inputCommand();
//1-5-1. start명령어를 받는 순간부터, ready가 default이며, start에 의해 ready to Running으로 넘어간다.
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
if (특정객체.isNotRunning()) {
break;
}
// (1) running중인 정보(board)를 가지고 finished상태로 만들도록 명령한 뒤
특정객체.end();
// (2) 이 때만(ready(X), finsihed(X) running to finished by .end() )시에만 게임결과를 출력한다.
// my) running -> finished 순간을 캐취해서 게임결과를 출력해줘야한다. (가만히 있는 finished는 출력할 필요도 없이 종료)
System.out.println("게임 하다가 끝났기 때문에, 게임 결과를 출력합니다.");
}
}
}
private static class 특정객체 {
private String state;
public 특정객체() {
// this.state = "running";
this.state = "ready"; // 1-5-2. start명령어가 있다면, ready가 기본이 된다.
}
public boolean isNotRunning() {
if (this.state.equals("running")) {
System.out.println("running상태입니다.");
return false;
}
System.out.println("ready or finished상태입니다.");
return true; // ready나 finished상태
}
public void end() {
System.out.println("상태가 running -> finished");
this.state = "finished";
}
}
}
03 아주 만약, 모든 분기마다 자기일 끝나고 맨 마지막에 공통로직을 처리해줘야한다면, 굳이 continue;(반복문의 ealry return)로 아래로 내려가는 것을 안 막는다.
각 분기 중 택1을 작업후, 다 제끼고 내려와, 분기없이 실행되는 로직(ex> 무한반복문 아니라면 while조건속에 들어갈 count++변수 업데이트?)
my) 반복문 속 분기이후 공통로직/업데이트로직이 있는 남아있다면, continue;를 안쓴다. 만약, 맨 아래 공통로직 없이 분기 택1의 로직만 일어난다면 continue;로 아래로 내려가는 것을 막아 검사조차 안되게 하자.
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final InputView inputView = new InputView();
final 특정객체 특정객체 = new 특정객체();
while (true) {
final String inputCommand = inputView.inputCommand();
if (inputCommand.equals("start")) {
특정객체.start();
System.out.println("게임을 시작합니다.");
//continue; // while continue 여부는 분기외에 아래 달릴 로직을 거치느냐 안거치느냐 차이
// -> [공통로직 ]있으면 continue를 빼고 거치게 하지만, 택1의 분기라면 continue;를 달아주자.
// -> 지금은 맨 아래 print가 공통로직이라고 치고 있으니 continue;를 제거하자.
}
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
if (특정객체.isNotRunning()) {
break;
}
특정객체.end();
System.out.println("게임 하다가 끝났기 때문에, 게임 결과를 출력합니다.");
}
// 공통로직을 매 입력-회전마다 거치는 경우에는 continue;를 쓰면 안된다.
System.out.println("공통로직입니다. 한바퀴돌고 재입력받기 직전입니다.");
}
}
while(true) 반복문 속 if break;의 메서드 추출
01 if 종료조건 break; 는 메서드 추출을 위해 -> if 종료조건 flag변수(Enum) Off처리; + continue;로 while조건문으로 보낸 뒤 -> while조건문에 flag검사( not isOff()? )로 변경한다.
break; 대신 돌아가는 로직 객체의 flag변수(enum)에 .end()처리를 하고, continue;로 아래론 못가고, while문으로 가서 조건 검사를 바로 하게 한다.
-
그림에선 boolean변수에 true/false를 주지만 캡슐화 및 확장성을 고려하여 enum으로 flag변수를 가지게 한다.
- 메인로직을 담당하는 객체에
flag(enum)변수를 항상 변할수있는 상태값으로 가지게 한다.

- 메인로직을 담당하는 객체에
while (true) {
final String inputCommand = inputView.inputCommand();
if (inputCommand.equals("start")) {
특정객체.start();
System.out.println("게임을 시작합니다.");
}
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
if (특정객체.isNotRunning()) {
//break;
특정객체.exit(); // flag isEnd = true;
continue; // break; 대신 밑으로 못내려가게 일단 막아주자.
}
특정객체.end();
System.out.println("게임 하다가 끝났기 때문에, 게임 결과를 출력합니다.");
}
if (inputCommand.equals("status")) {
System.out.println("갑자기 결과를 출력합니다. ");
}
}
private static class 특정객체 {
private String state;
private boolean isEnd;
//...
public void exit() {
this.isEnd = true;
}
}
02 flag .off() 처리후 continue;로 올라간 조건문 검사를 while (true) -> 플래그변수가.isOff()인지 검사로 변경한다.
-
flag isEnd = true;하는 순간, 다continue(or return되서 ) while 조건문으로 보내야한다- 조건문에서는 flag를 확인하여 입력과 반복을 종료시킨다
-
반복문은
break;였던 자리가 flag에 걸려서 종료되기 전까지 돌아야한다-
!를 달아준다.
-
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final InputView inputView = new InputView();
final 특정객체 특정객체 = new 특정객체();
//while (true) {
while (!특정객체.isEnd()) {
final String inputCommand = inputView.inputCommand();
if (inputCommand.equals("start")) {
특정객체.start();
System.out.println("게임을 시작합니다.");
}
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
if (특정객체.isNotRunning()) {
//break;
특정객체.exit(); // flag isEnd = true;
continue; // break; 대신 밑으로 못내려가게 일단 막아주자.
}
특정객체.end();
System.out.println("게임 하다가 끝났기 때문에, 게임 결과를 출력합니다.");
}
if (inputCommand.equals("status")) {
System.out.println("갑자기 결과를 출력합니다. ");
}
}
}
private static class 특정객체 {
private String state;
private boolean isEnd;
//...
public boolean isEnd() {
return this.isEnd;
}
}
}
03 if break; -> if flagOff + contine + while flag isOff()검사 해줬어도 if조건식에 extract method는 depth를 못 줄인다
-
if + if전체를 추출하려고 하면,- 바깥if의
boolean문만 파라미터 추출 -> t/f 메서드로 추출하여 통째로 넘어간다
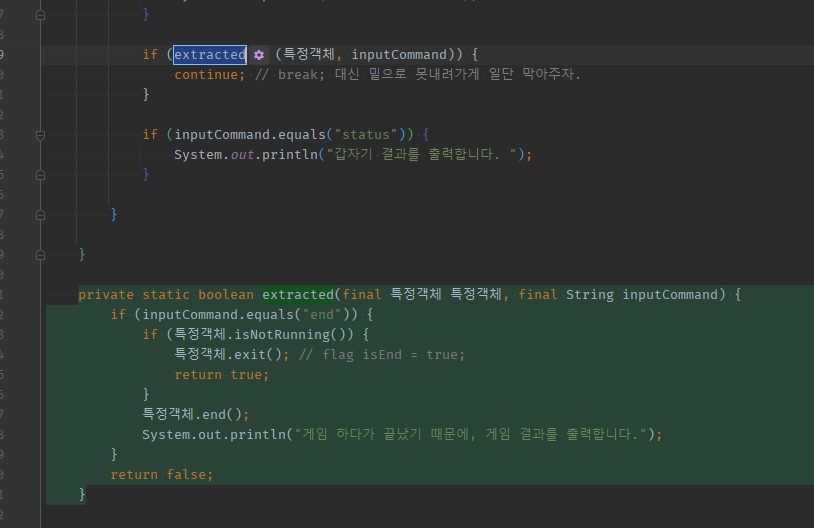
- 바깥if의
-
내부if부분만 추출하려고 하면-
내부 if 조건문 속
boolean문만 파라미터 추출 -> true/false의 메서드 추출하여 통째로 넘어간다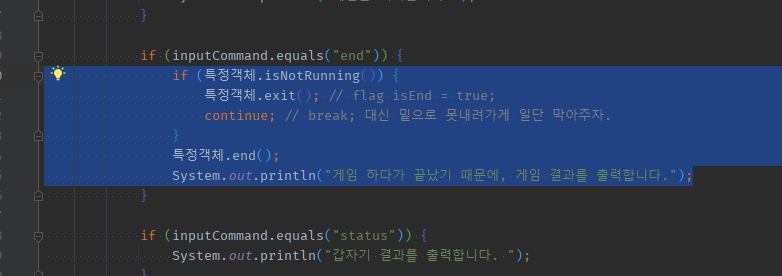
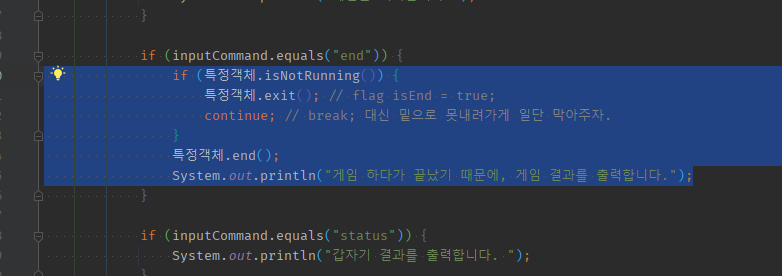
-
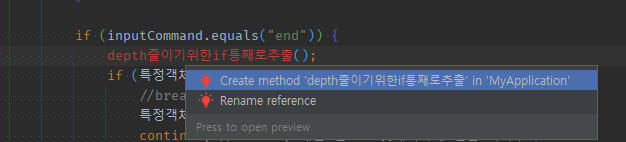
04 if조건문의 메서드추출은 수동으로 통째로
if 문 위에 추출할 메서드를 빨간줄 작성후 생성
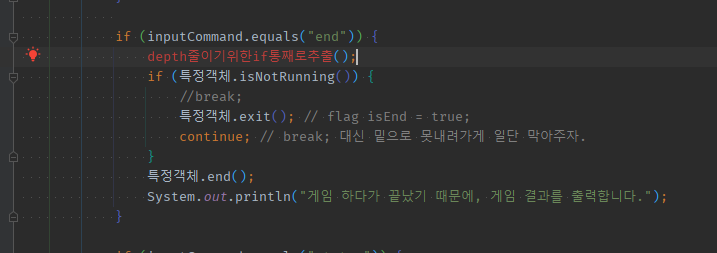
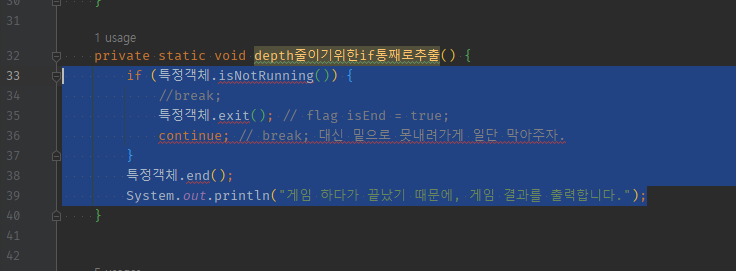
05 복붙으로 코드 옮겨가고 flag변수.Off() 처리후 continue; 대신 -> 1) early return; + 2) 추출메서드를 while문 맨 뒤에 배치하여 flag처리 직후 while조건문 검사하는 continue;효과내기
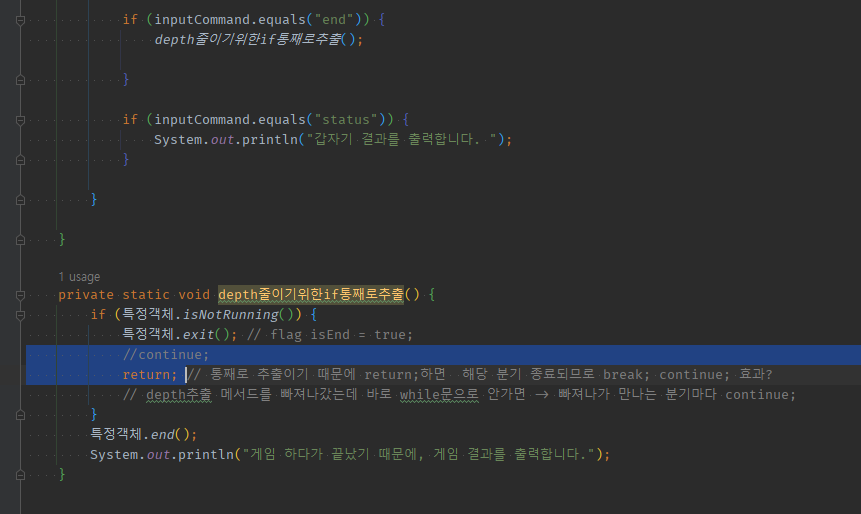
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final InputView inputView = new InputView();
final 특정객체 특정객체 = new 특정객체();
//while (true) {
while (!특정객체.isEnd()) {
final String inputCommand = inputView.inputCommand();
if (inputCommand.equals("start")) {
특정객체.start();
System.out.println("게임을 시작합니다.");
}
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
depth줄이기위한if통째로추출();
}
if (inputCommand.equals("status")) {
System.out.println("갑자기 결과를 출력합니다. ");
}
}
}
private static void depth줄이기위한if통째로추출() {
if (특정객체.isNotRunning()) {
특정객체.exit(); // flag isEnd = true;
//continue;
return; // 통째로 추출이기 때문에 return;하면 해당 분기 종료되므로 break; continue; early return기능은 있지만 + flag처리 직후 while조건문 검사기능은 구현불가능하다.
// -> 지금은 분기 택1의 로직만 일어나므로 바로 while문 검사하러 간다.
// -> 만약, return 아래로 더 내려간다면? 남은로직 or 공통로직이 있다면? -> continue;를 return;후에 처버려야할듯?
// depth추출 메서드를 빠져나갔는데 바로 while문으로 안가면 -> 빠져나가 만나는 분기마다 continue;
}
특정객체.end();
System.out.println("게임 하다가 끝났기 때문에, 게임 결과를 출력합니다.");
}
while문을 재귀로 고치기
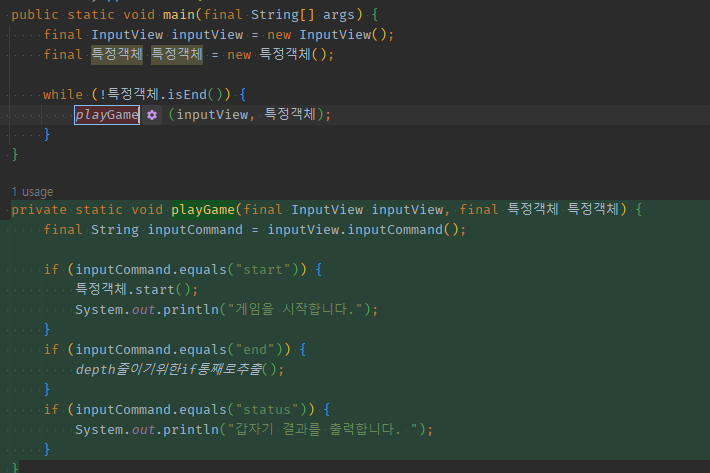
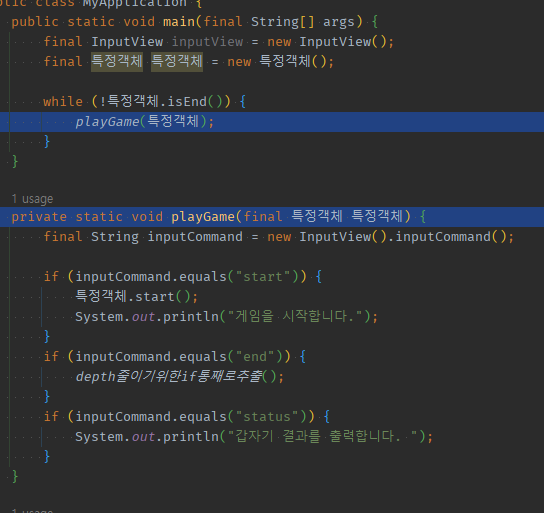
01 while속 돌아가는 모든 (분기)로직들을 통으로 1개 메서드로 추출
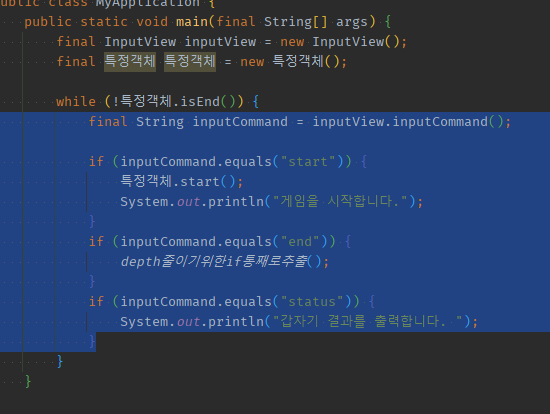
-
inputView는 원래 컨트롤러 속이라면 상태값을 가지고 있을 예정이기 때문에 일단 파라미터에 제외시켜야함
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final InputView inputView = new InputView();
final 특정객체 특정객체 = new 특정객체();
while (!특정객체.isEnd()) {
playGame(특정객체);
}
}
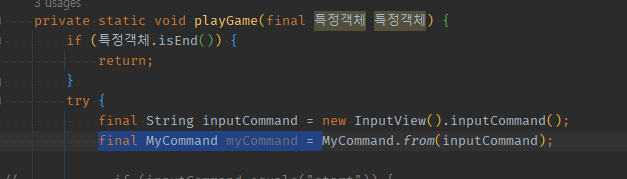
private static void playGame(final 특정객체 특정객체) {
final String inputCommand = new InputView().inputCommand();
if (inputCommand.equals("start")) {
특정객체.start();
System.out.println("게임을 시작합니다.");
}
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
depth줄이기위한if통째로추출();
}
if (inputCommand.equals("status")) {
System.out.println("갑자기 결과를 출력합니다. ");
}
}
02 while !EndFlag 조건문 = flag 확인문 -> 재귀 속 break(EndFlag)하는 종착역으로서 먼저 if early return로 정의해주기
-
기존 while (
! 끝나는 조건) -> if끝나는조건: 재귀함수 return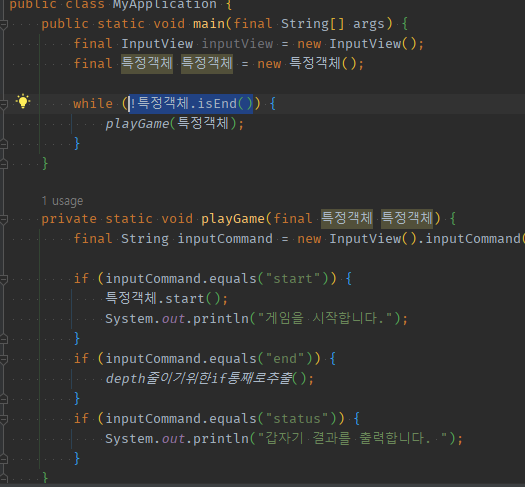
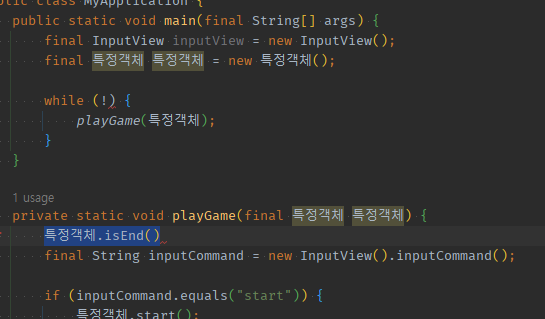
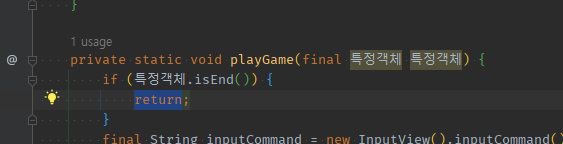
재귀함수는 종착역인 if flag isEND() :return;이 반복문의 break와 동일하게 반복을 제거한다
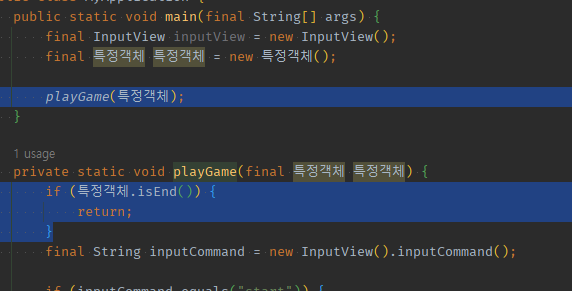
03 반복되던 로직의 if return종착역까지 완성됬으면 -> 함수 끝날 때 자신(메서드) 부르기
내부 if return의 종착역만 있다면, 편하게 마지막에 한번 더 호출하여 반복하는 재귀함수를 만들 수 있다.
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final 특정객체 특정객체 = new 특정객체();
playGame(특정객체);
}
private static void playGame(final 특정객체 특정객체) {
if (특정객체.isEnd()) {
return;
}
final String inputCommand = new InputView().inputCommand();
if (inputCommand.equals("start")) {
특정객체.start();
System.out.println("게임을 시작합니다.");
}
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
depth줄이기위한if통째로추출();
}
if (inputCommand.equals("status")) {
System.out.println("갑자기 결과를 출력합니다. ");
}
playGame(특정객체);
}
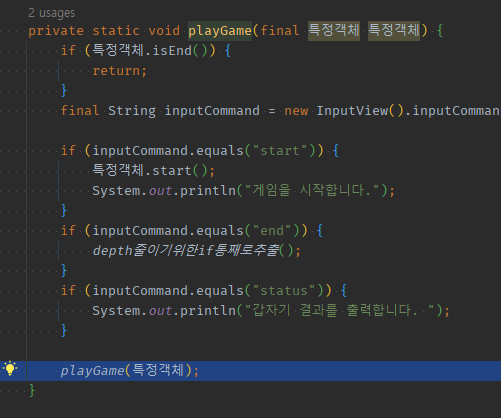
04 while to 재귀로 만든 이유 -> inputView가 포함된&&입력받는 것부터 시작하는 로직은 try로 살펴보는 시작이 input부터이면서 && catch시 다시 input부터 시작하도록 재귀함수형태를 만들어하므로
01 1번만 성공적으로 input받는 로직과 다르게 try 끝에 성공했어도 반복되기 위해 재귀호출을 한다. 1번만 호출되려면 catch로 실패시 재귀호출하여 시도함
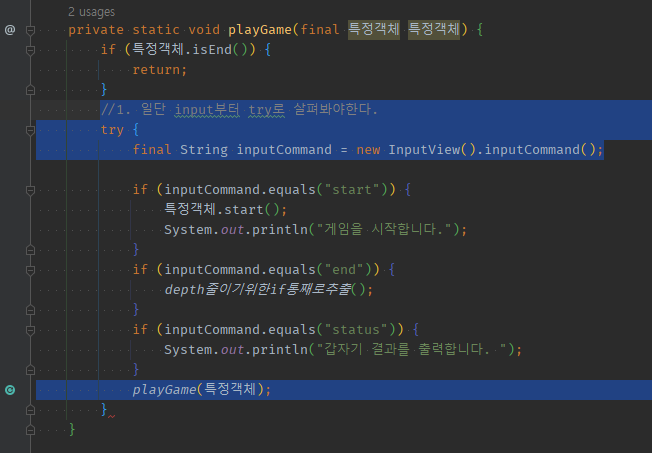
02 catch에서 실패한 경우 input부터 다시 받기 위한 재귀호출 vs try끝에 thr없는 성공했는데도 반복을 위한 재귀호출
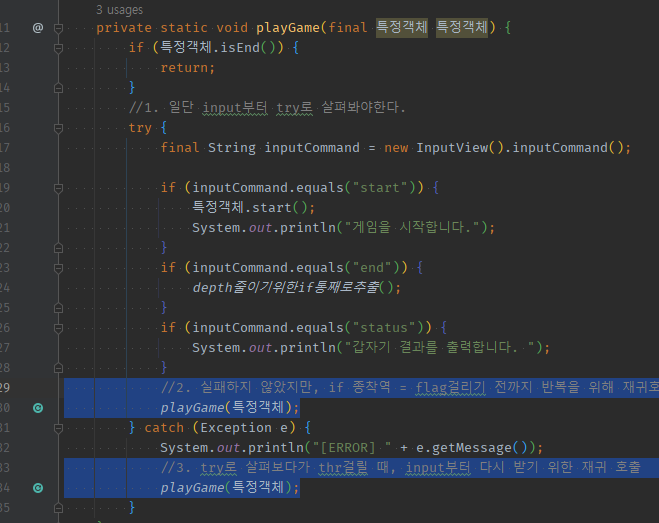
private static void playGame(final 특정객체 특정객체) {
if (특정객체.isEnd()) {
return;
}
//1. 일단 input부터 try로 살펴봐야한다.
try {
final String inputCommand = new InputView().inputCommand();
if (inputCommand.equals("start")) {
특정객체.start();
System.out.println("게임을 시작합니다.");
}
if (inputCommand.equals("end")) {
depth줄이기위한if통째로추출();
}
if (inputCommand.equals("status")) {
System.out.println("갑자기 결과를 출력합니다. ");
}
//2. 실패하지 않았지만, if 종착역 = flag걸리기 전까지 반복을 위해 재귀호출
playGame(특정객체);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR] " + e.getMessage());
//3. try로 [input부터 시작하는 로직]살펴보다가 thr걸릴 때, [input부터 다시 받기 위한 재귀 호출]
playGame(특정객체);
}
}
my) input부터 시작하는 로직을 재귀함수로 만들면, try input부터 살펴보는 중에 실패하면 -> catch에서 재귀호출하여 다시 input부터 시작할 수 있다.
Enum과 명령어 문자열 캡슐화 + 외부input시 검증까지
01 갯수가 정해진 input명령어들(문자열상수)은 분기비교에 사용시 enum객체필드에 캡슐화해놓고 사용하기
- 명령어 객체 -> 복붙해서 문자열에 넣고 소문자로 만들기
02 일단은 분기 속 input문자열 vs 비교문자열 -> Enum from정펙매( input ) VS enum객체로 바꿔서 비교하기
my) 컨트롤러에서 상수 쓰지말고input을 정펙매에 넣어 찾아진 ENum객체 vs 상수캡슐화한 enum으로 비교 + enum은 스태틱변수라 메모리값 1개 -> equals 안써도 된다.
-
input-> 정펙메에서전체 돌기 + filter로 해당enum객체를 구분하여 생성한다
- 마찬가지로
- input ->
enum.from(input) - “문자열” ->
Enum.문자열캡슐화한객체
- input ->
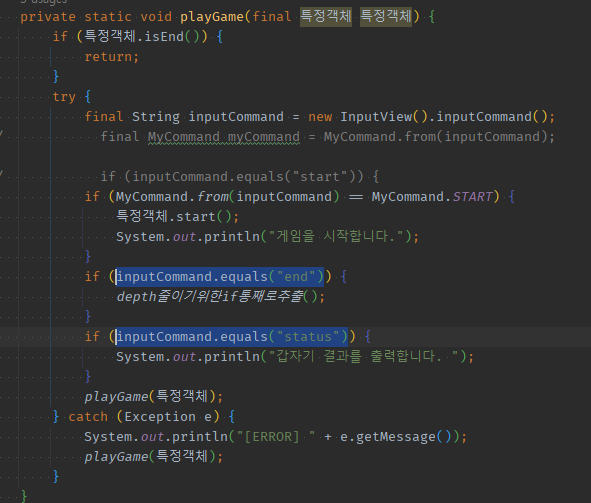
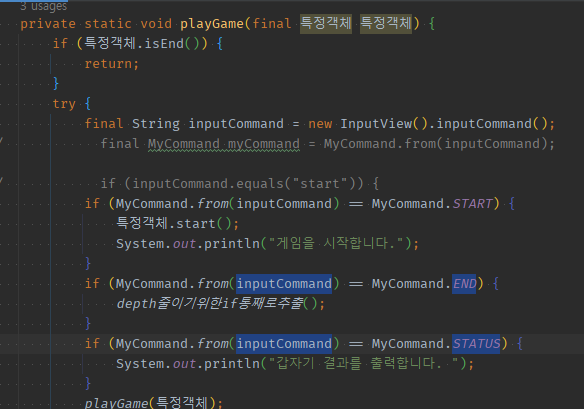
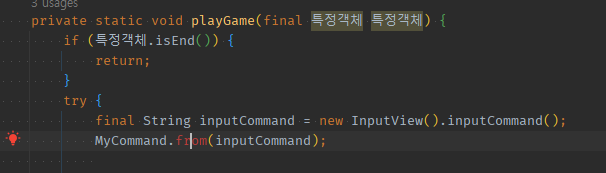
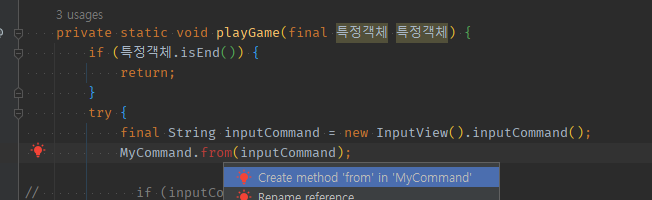
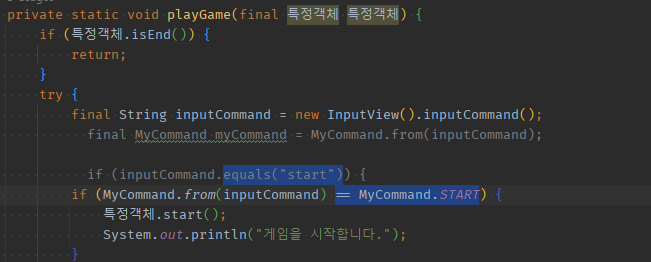
private static void playGame(final 특정객체 특정객체) {
if (특정객체.isEnd()) {
return;
}
try {
final String inputCommand = new InputView().inputCommand();
//if (inputCommand.equals("start")) {
if (MyCommand.from(inputCommand) == MyCommand.START) {
특정객체.start();
System.out.println("게임을 시작합니다.");
}
if (MyCommand.from(inputCommand) == MyCommand.END) {
depth줄이기위한if통째로추출();
}
if (MyCommand.from(inputCommand) == MyCommand.STATUS) {
System.out.println("갑자기 결과를 출력합니다. ");
}
playGame(특정객체);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR] " + e.getMessage());
playGame(특정객체);
}
}
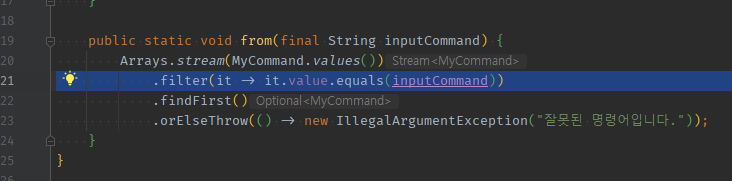
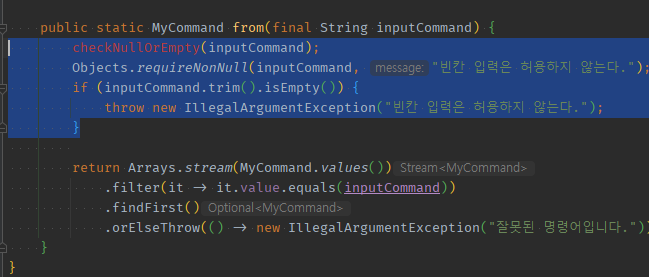
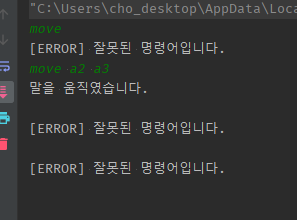
03 외부 input으로 찾는 Enum정펙매은 기본적으로 이넘객체들에 캡슐화되어매핑된 문자열들로 -> contains thr 검증이 자동 되며 + 외부input NullOrEmpty를 여기서도 할 수 있다.
enum 외부input 검증01 - 기본적으로 filter사용 == contains 검증 : filter에서 외부input이 내부캡슐화된 문자열에 속하지 않아 못찾으면 orElseThrow에서 에러thr나게 됨.
-
외부 input-> Enum정펙매 from -> filter(캡슐화된 문자열.equals외부 input)- filter에 안걸리는 것 = 캡슐화된 문자열에 속하지 않은 것 -> thr
- try로 input부터 보고있었으면 검증되서 다시 받는다.
enum 외부input 검증02 - 추가적으로 checkNullOrEmpty : 찾아들어가기전에 외부 input의 nullOrEmpty검사를 정펙매 여기서 해줄 수 있다. 왜냐? 재귀에서 input부터 처다보고 있는 상황이니까 반복됨.
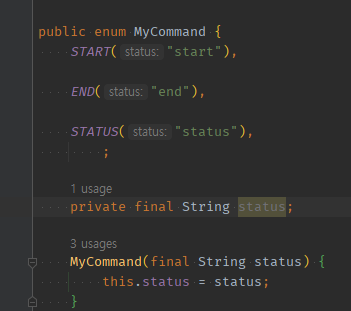
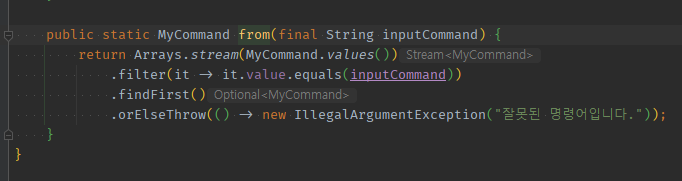
public enum MyCommand {
START("start"),
END("end"),
STATUS("status"),
;
private final String value;
MyCommand(final String value) {
this.value = value;
}
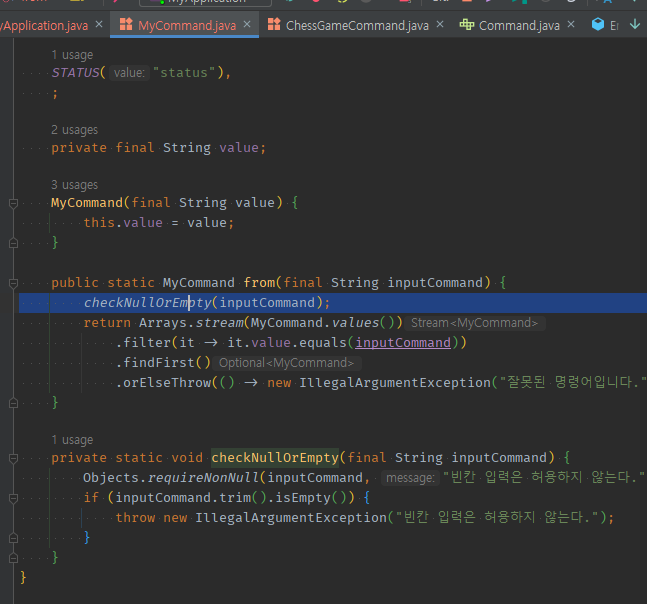
public static MyCommand from(final String inputCommand) {
checkNullOrEmpty(inputCommand);
return Arrays.stream(MyCommand.values())
.filter(it -> it.value.equals(inputCommand))
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 명령어입니다."));
}
private static void checkNullOrEmpty(final String inputCommand) {
Objects.requireNonNull(inputCommand, "빈칸 입력은 허용하지 않는다.");
if (inputCommand.trim().isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("빈칸 입력은 허용하지 않는다.");
}
}
}
외부input으로 찾는 Enum의 filter에 정규식을 쓰면?
01 equals()는 Pattern.matches()에 포함되며 일치를 포함하여 일치를 포함하여 패턴을 가지는 문자열도 처리
-
추가 캡슐화 문자열 -> Enum객체가 생겼다.
- 어차피 개별 비교라서 상관은 없다
-
하지만 개별비교가 equals에서 패턴매칭으로 달라진다면?
- 상관없다.
패턴매칭은 equals를 포함한다
- 상관없다.
-
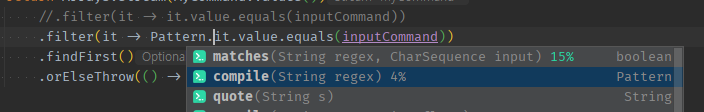
원래 Pattern 클래스는 .complie()로 패턴을 만들고
-
이후 Matcher.matches()를 써서 비교했던 것 같은데
- Matches없이 한번에 matches()로 t/f를 반환시킬 수 있다.
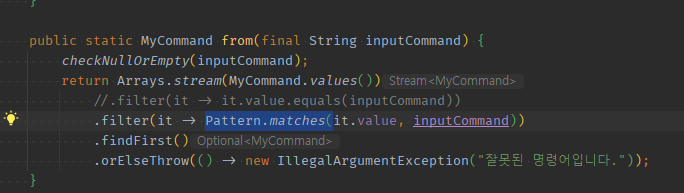
-
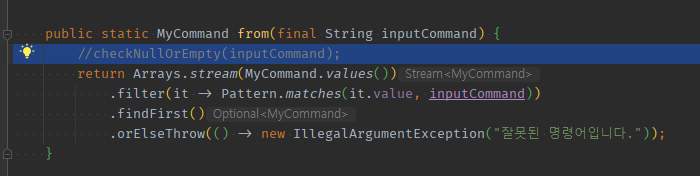
02 equals() -> Pattern.matches()로 교환했다면 nullOrempty 검증도 패턴매칭에 포함된다.
enum 외부input 검증03 - Patter.matches()를 쓸 경우 : nullOrEmpty검증도 매칭안되는 것에 걸려 검증된다.
enum으로 분기 제거까지 적용하려면?
외부input + 정펙매로 해당 enum객체 -> 해당 분기로직을 분기별 해당enum field에 함수형인터페이스 필드-> 전략객체들 생성자 -> 호출까지 따로 or 함수형인터페이스 1개 지정 -> 람다식 가져가야한다.
01 분기 제거를 가정하려면, 추상화된 객체(인페orEnum).메서드()로 빨간줄을 만든다.
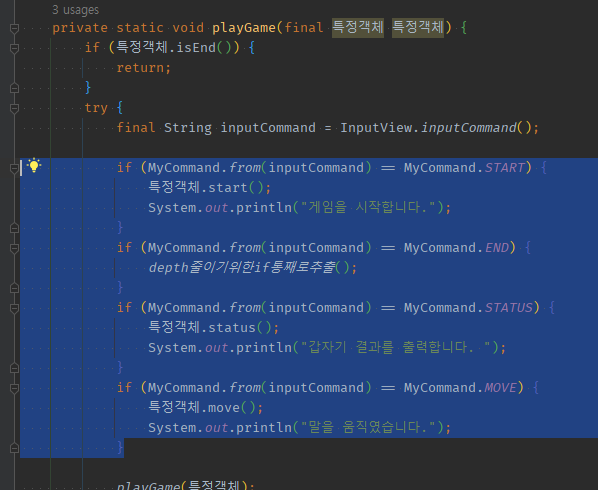
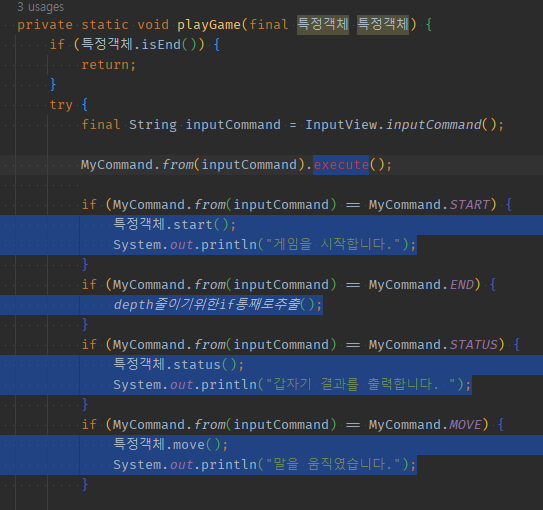
01 if 정펙매( input ) == 예상Enum의 분기마다 알아서 작동하게 하려면, 분기내 로직을 모두 해당Enum의 field로 가져올 수 있는지 봐야한다.
private boolean isRunning() {
if (gameSwitch.isOff()) {
return false;
}
return !isNotRunning();
}
private boolean isStatusInRunning() {
if (gameSwitch.isOff()) {
return false;
}
return state.isStatus();
}
private boolean isEndInRunning() {
if (gameSwitch.isOff()) {
return false;
}
return state.isFinished();
}