분기문과 드모르간 법칙
A && B 이전에 return되도록 ||로 만들어 찢자.
📜 제목으로 보기
- 분기문에 적용하는 드모르간
- boolean식 분기 적용법: ` && -> ||으로 분리후 -> 드모르간 적용`
- 01 return A && B 로 작성해놓았다면, replace with ||로 분리한다.
- 02 가장 바깥 !( )는 무시한 체, return || 는 순서가 중요 -> 아래쪽 순서대로 if return true문으로 찢는다.
- 03 return || 오른쪽 끝까지 모두 통과X -> false 이므로 if return true; 여러개 맨 아래 까지 통과x시 -> return false;
- 04 무시했던 바깥 !()을 적용시키려고 return true/false 반대로작성하기
- 05 암기 및 정리: (if를 다지난 마지막자리에 주석 //A && B와 함께 자동 자리에)retun true를 주고 ->if notA return false -> if notB return false;
- 06 사실 boolean이라면 if not A -> (자동A) return B를 해버리면 된다. (로직일 경우 not B도 개별 처리해줘야하니까 다름)
- 기본 로직 적용법 및 암기법: A && B는 if notA -> if notB -> 맨마지막 자동 A && B에서 처리되도록
- my) A && B의 처리는 if A부터 처리 못한다?(if not A) -> 바로 탈락(return false;) 시킨다. OR로 본다면 앞에거 먼저 만족하면 return True로 전체 종료되는 개념과 유사하다.
- my) boolean A&&B 이라면, notA || notB + 원랜 앞에것 통과시 true로 끝 But 여기선 !땜에 return false; -> A부터 만족 못할시 빠르게 false로 종료처리되도록 -> if로 찢어 if not return false시켜버린다.
- my) boolean이라면, if not 앞쪽A -> return false; 이후 (if문 아래쪽은 자동 A &&상태이므로) 마지막 분기식은 바로 return (자동A&&) B해버려도 된다. ( if not B로직이 필요없는 상황)
- my) boolean처럼 로직도 if notA return -> if notB return -> (자동 A && B) return 을 사용한다.
- my-역) if return false -> A && B 조건에서 앞쪽 A를 먼저 만족시키지못해 애초에 탈락이구나 -> not A 상황이라서 && B보기전에 빨리 거르기 + 밑으로는 (A &&)상태구나
- my-역) if return false + return B -> A||B의 앞쪽 A라 notA라 거르고, 밑에서 A && B 이며, true시 true니까.. A && B시 true리턴이구나..
- 해석 연습해보기
분기문에 적용하는 드모르간
문제 상황
-
루피 피드백 중 1개를 발취
@Override public final boolean isMovable(Position source, Position target, ChessBoard chessBoard) { return !existSameColorPiece(source, target, chessBoard) && isMovableByDirection(source, target); } -
드모르간의 법칙을 참고하면 아래와 같이 변경할 수 있을 것 같아요.
-
&&: 작성자는 이해하기 쉬운 경우이나- 라인 수는 줄어들지만 라인을 끝까지 다 읽어봐야 이해할 수 있을 것 같아요.
-
&& -> || -> if문 분기로 찢: 반대로 분리해서 if 문으로 연산을 제거하면- 라인 수는 늘어나지만 어떤 조건에서 if 조건을 실행하는지 좀 더 이해하기 쉬워질 것 같은데요.
- 저는 최대한 and 연산을 지양하고 or
연산을 변환한 뒤 if 문으로 분리하는 편 입니다 ㅎㅎ
@Override public final boolean isMovable(Position source, Position target, ChessBoard chessBoard) { if (existSameColorPiece(source, target, chessBoard)) { return false; } if (!isMovableByDirection(source, target)) { return false; } return true; } -
boolean식 분기 적용법: ` && -> ||으로 분리후 -> 드모르간 적용`
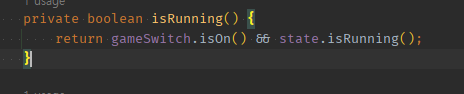
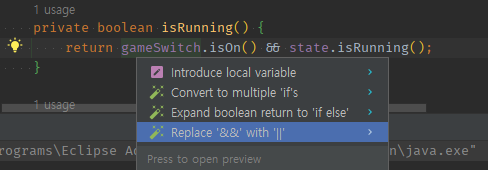
01 return A && B 로 작성해놓았다면, replace with ||로 분리한다.
private boolean isRunning() {
return gameSwitch.isOn() && state.isRunning();
}
private boolean isRunning() {
return !(!gameSwitch.isOn() || !state.isRunning());
}
02 가장 바깥 !( )는 무시한 체, return || 는 순서가 중요 -> 아래쪽 순서대로 if return true문으로 찢는다.
-
||의 or는앞에 것 통과하면 뒤에것 안보고 통과하는 성격이 있다.-
if 앞에 것 통과시 return되도로 if문으로 찢어보자.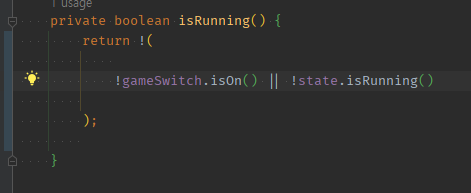
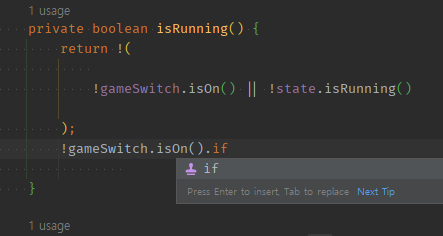
- 아래에다가 점진적으로 찢어보자.
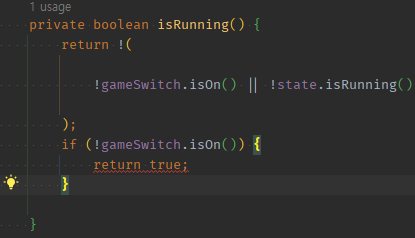
-
` ||에서 앞에것 통과 못했으면 == if 분기에서 위에 것 통과 못했으면으로 동치다 -> if A? ||오른쪽orif아래쪽은 자동notA`
-
||에서 앞에것 통과 못했으면==if 분기에서 위에 것 통과 못했으면으로 동치다- 순서가 중요한
||와if분기
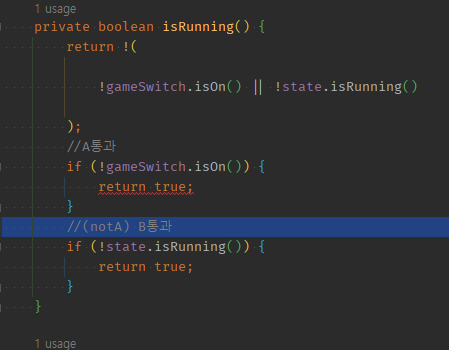
- 순서가 중요한
private boolean isRunning() {
return !(
!gameSwitch.isOn() || !state.isRunning()
);
//A통과
if (!gameSwitch.isOn()) {
return true;
}
//(notA) B통과
if (!state.isRunning()) {
return true;
}
}
03 return || 오른쪽 끝까지 모두 통과X -> false 이므로 if return true; 여러개 맨 아래 까지 통과x시 -> return false;
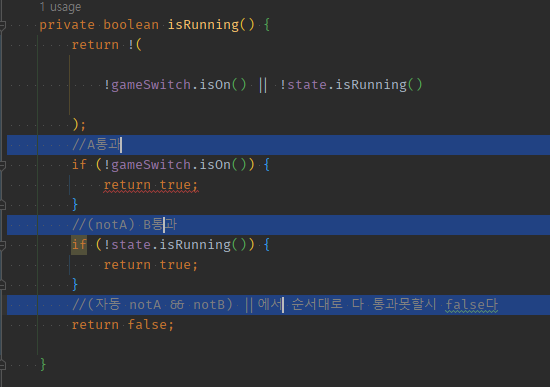
private boolean isRunning() {
return !(
!gameSwitch.isOn() || !state.isRunning()
);
//A통과
if (!gameSwitch.isOn()) {
return true;
}
//(notA) B통과
if (!state.isRunning()) {
return true;
}
//(자동 notA && notB) ||에서 순서대로 다 통과못할시 false다
return false;
}
04 무시했던 바깥 !()을 적용시키려고 return true/false 반대로작성하기
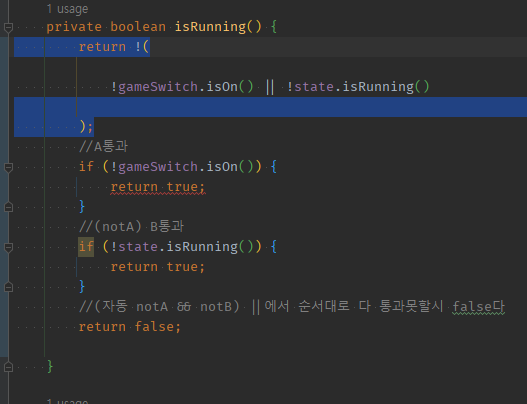
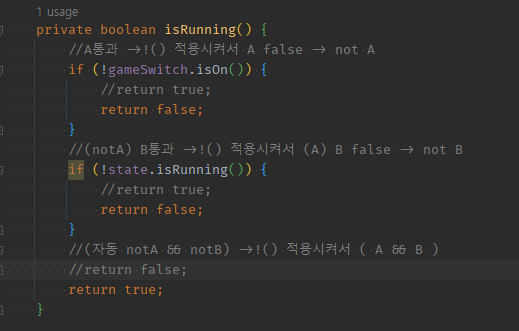
private boolean isRunning() {
//A통과 ->!() 적용시켜서 A false -> not A
if (!gameSwitch.isOn()) {
//return true;
return false;
}
//(notA) B통과 ->!() 적용시켜서 (A) B false -> not B
if (!state.isRunning()) {
//return true;
return false;
}
//(자동 notA && notB) ->!() 적용시켜서 ( A && B )
//return false;
return true;
}
05 암기 및 정리: (if를 다지난 마지막자리에 주석 //A && B와 함께 자동 자리에)retun true를 주고 ->if notA return false -> if notB return false;
06 사실 boolean이라면 if not A -> (자동A) return B를 해버리면 된다. (로직일 경우 not B도 개별 처리해줘야하니까 다름)
기본 로직 적용법 및 암기법: A && B는 if notA -> if notB -> 맨마지막 자동 A && B에서 처리되도록
예시1) row && col의 대각선
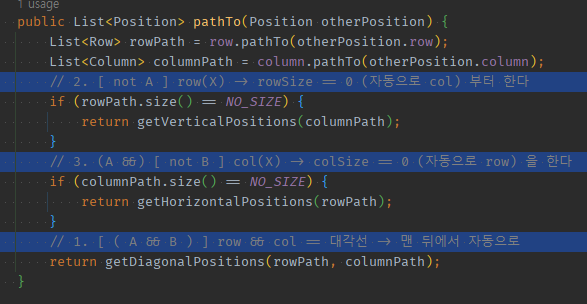
public List<Position> pathTo(Position otherPosition) {
List<Row> rowPath = row.pathTo(otherPosition.row);
List<Column> columnPath = column.pathTo(otherPosition.column);
// 2. [ not A ] row(X) -> rowSize == 0 (자동으로 col) 부터 한다
if (rowPath.size() == NO_SIZE) {
return getVerticalPositions(columnPath);
}
// 3. (A &&) [ not B ] col(X) -> colSize == 0 (자동으로 row) 을 한다
if (columnPath.size() == NO_SIZE) {
return getHorizontalPositions(rowPath);
}
// 1. [ ( A && B ) ] row && col == 대각선 -> 맨 뒤에서 자동으로
return getDiagonalPositions(rowPath, columnPath);
}
예시2) 누구 king이 잡혔냐? -> (자동 둘다 &&안잡힌 상황)
private static GameResult findWinner(final Board board,
final double statusOfWhite,
final double statusOfBlack) {
// 2. not A -> black잡힘
if (board.hasBlackKingCaptured()) {
return GameResult.WHITE_WIN;
}
// 3. (black안잡혔는데 ) not B -> white잡힘
if (board.hasWhiteKingCaptured()) {
return GameResult.BLACK_WIN;
}
// 1. ( 자동 black안잡힘 && white안잡힘 ) -> 점수 비교 로직
return getResultWhenNoKingCaptured(statusOfWhite, statusOfBlack);
}
예시3) boolean에서 A && B
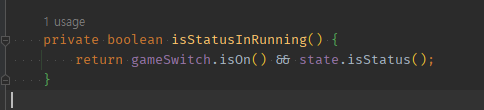
private boolean isStatusInRunning() {
return gameSwitch.isOn() && state.isStatus();
}
01 (자동으로 될 A && B를 주석처리와 함께)맨 끝에서 return true
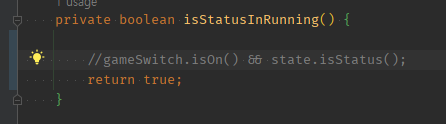
private boolean isStatusInRunning() {
//gameSwitch.isOn() && state.isStatus();
return true;
}
02 if not A를 만들고 return false;
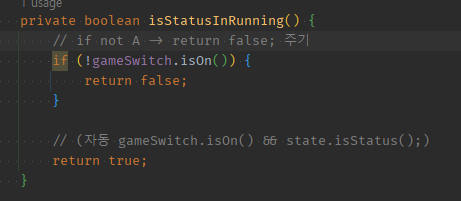
private boolean isStatusInRunning() {
// if not A -> return false; 주기
if (!gameSwitch.isOn()) {
return false;
}
// (자동 gameSwitch.isOn() && state.isStatus();)
return true;
}
03 if not B 만들고 return false;
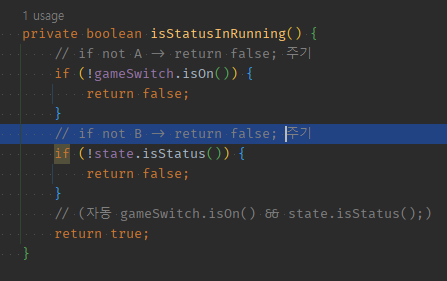
private boolean isStatusInRunning() {
// if not A -> return false; 주기
if (!gameSwitch.isOn()) {
return false;
}
// if not B -> return false; 주기
if (!state.isStatus()) {
return false;
}
// (자동 gameSwitch.isOn() && state.isStatus();)
return true;
}
04 boolean이라 따로 로직이 필요없다면 if not A return false;후 -> return (자동 A &&) B

private boolean isStatusInRunning() {
// if not A -> return false; 주기
if (!gameSwitch.isOn()) {
return false;
}
// if not B -> return false; 주기
//if (!state.isStatus()) {
// return false;
//}
// (자동 A && B == gameSwitch.isOn() && state.isStatus();)
//return true;
// (자동A )
return state.isStatus();
}
my) A && B의 처리는 if A부터 처리 못한다?(if not A) -> 바로 탈락(return false;) 시킨다. OR로 본다면 앞에거 먼저 만족하면 return True로 전체 종료되는 개념과 유사하다.
my) boolean A&&B 이라면, notA || notB + 원랜 앞에것 통과시 true로 끝 But 여기선 !땜에 return false; -> A부터 만족 못할시 빠르게 false로 종료처리되도록 -> if로 찢어 if not return false시켜버린다.
my) boolean이라면, if not 앞쪽A -> return false; 이후 (if문 아래쪽은 자동 A &&상태이므로) 마지막 분기식은 바로 return (자동A&&) B해버려도 된다. ( if not B로직이 필요없는 상황)
my) boolean처럼 로직도 if notA return -> if notB return -> (자동 A && B) return 을 사용한다.
my-역) if return false -> A && B 조건에서 앞쪽 A를 먼저 만족시키지못해 애초에 탈락이구나 -> not A 상황이라서 && B보기전에 빨리 거르기 + 밑으로는 (A &&)상태구나
my-역) if return false + return B -> A||B의 앞쪽 A라 notA라 거르고, 밑에서 A && B 이며, true시 true니까.. A && B시 true리턴이구나..
해석 연습해보기
BOOLEAN 中 and 조건문
private boolean isRunning() {
if (gameSwitch.isOff()) {
return false; // 1. return false -> end boolean식이 전제이며, A && B에서 A를 만족못시키는 [A && B에서 not A라서 먼저 false;로 걸러지는구나]
}
// 2. 자동 not A(! .isOff() == isOn()) 상태 && 로서 A(스위치On)&&이면서 B가 와야하구나.
// 3. 만약, 조건식이 1개가 남았다면 바로 return 조건문으로 끝낸다.
// -> [ (자동 isOn &&) !notRunning 이어야 end조건의 boolean식이 최종 true가 되는 구나]
// -> is ON && running 상태여야 true
return !isNotRunning();
}
```java
private boolean isStatusInRunning() {
if (gameSwitch.isOff()) {
return false;//1. early false -> and조건에서 빨리 걸러지는 상황으로 [앞쪽 not A -> off ]
}
//2. (자동 A -> on &&) 상태에서 if status상태여야 true구나.
return state.isStatus();
}
private boolean isEndInRunning() {
if (gameSwitch.isOff()) {
return false; // 1. not A 가 off로 먼저 걸러진다 -> A = on상태 &&
}
//2. on && finihsed상태여야 true
return state.isFinished();
}
BOOLEAN이 아닌 단순 경우의 수라면? -> 마지막 경우의수만 자동으로 가져간다.?! -> 복잡한 조건을 뒤에서 if없이 자동으로 가져가게 하자.
- A OR B OR C 경우의수: 편한 순서대로 ealry return하면서
마지막 경우의 수만 if없이 자동으로 가져간다- 참고: boolean
OR 조건문-> (이왕이면 잘 걸리는 것을 앞A에 배치해놓고)early true return으로 빨리 끝내기 (&&조건문시 앞에것부터 early false return처럼)
- 참고: boolean
public void move(Position beforePosition, Position afterPosition) {
Piece beforePiece = this.value.get(beforePosition);
// 로직 or : 순서 상관없이 [early return] + 마지막만 자동 경우의수로 가져가기**
// 단순 같은위상의 3가지 경우의 수 -> 순서상관엇이 if A return 로직A; if B return 로직B; (if없이 자동 자동3번째) 로직C;
// A: after에 빈칸이 있을 경우
if (isMoveToBlank(afterPosition)) {
beforePiece.move(beforePosition, afterPosition, moveFunction(beforePosition, afterPosition));
return;
}
// B: after에 적이 있을 경우
if (isMoveToOtherCampPiece(beforePosition, afterPosition)) {
beforePiece.capture(beforePosition, afterPosition, moveFunction(beforePosition, afterPosition));
return;
}
// C: (자동 빈칸도X 적X) -> (자동 after에 같은편이 있을 경우)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(CANT_MOVE_TO_SAME_CAMP);
}
- A OR B OR C -> A+B OR C로 통합된 경우 -> 마찬가지 마지막 경우의수만 if없이 자동
- if OR의 경우의수 2개를 통합했더니 -> A와 B의 로직이 다르면, 내부에서 다시 나눠야하는 부작용 있었음.
- A+B통합이 더 크므로, 차라리 C OR A+B로 보고 규모가 작은 것을 앞에 배치시키면
if문 없이 자동이 편해짐(아래서 함)
public void move(Position beforePosition, Position afterPosition) {
// 빈칸 + 적의 내부로직이 통합됨 OR로 연결됨 - ( A OR B = D)
// D OR C -> if D return 로직D; (자동C)-> if A return(true); 자동B
if (board.get(beforePosition).isNullPiece() || !board.get(beforePosition)
.isSameCampWith(board.get(afterPosition))) {
movePiece(beforePosition, afterPosition);
return; // OR는 early (true) return 필수다. 로직이라면 그냥 earyl return;필수
}
// (자동C: 같은 진영의 기물인 경우)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(CANT_MOVE_TO_SAME_CAMP);
}
- A+B OR C라면 규모가 작은 C를 먼저 ealry return
public void move(final Positions positions) {
if (isAfterPieceSameCamp(positions)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(CANT_MOVE_TO_SAME_CAMP);
}
movePiece(positions);
}