함수형인터페이스 만들어 로직넘기기
로직을 특정 객체의 행위에 넘기고 싶을 때 + 유용패턴3
📜 제목으로 보기
- 문제 상황
- 예시1: thr가능성있는 타객체.메세지() 이후의 로직들을 타객체메세지보낼때 같이 보내기
- 01 넘기고 싶은 로직을 () -> {}; 람다를 이용하여 함형을 만든다.
- 02 타 객체가 내부에 사용됬다면, 람다식의 (input) -> {};으로 받아 -> 함형.메서드( this );로 사용되도록 해야한다.
- 03 람다식의 input이 정해지면, [변수추출]로 함형종류 + inputType을 지정해준다 -> 변수추출하면 메서드 추출도 응답값 지정이 잘됨.
- 04 타 객체의 메서드(인자)로 넘겨주기 위해, 함형의 = 제외한 우항만 메서드 추출
- 05 추출한 로직의 함형을, 타객체 메서드에 건네줘서 -> 내부에서 this를 사용해 실행되도록 옮긴다.
- 06 함형으로 로직을 넘겨받은 타 객체는 내부에서 (this)를 인자로 주고 호출한다
- 예시2: 아래쪽 분기별 OutputView 로직이 도메인 샌드위치 사이에 위치한 경우 -> Runnable?객체면 Consumer?로 위쪽 도메인 메서드 인자에 함형메서드로 쏴서 넘겨주기
- [람다식을 통한 함형]이 유용할 경우 3가지
문제 상황
어떤 객체 로직이 [타 객체.행위() 성공여부]에 따라 갈린다면, 응답값을 억지로 받지말고 -> [타 객체 context] 내부로 넘기자
public final class Board {
private void movePiece(final Position beforePosition, final Position afterPosition) {
Piece beforePiece = this.value.get(beforePosition);
beforePiece.move(beforePosition, afterPosition);
// .move()의 결과에 따라 실행/안실행되는 -> piece내부로 넘겨주고 싶은 Board 로직
this.value.put(afterPosition, beforePiece);
this.value.put(beforePosition, new NullPiece(null));
}
- Board의 this.value(
map)에 pu하는 로직을- **타 객체인
beforePiece.move( , )의 성공여부에 따라 실행시키고 싶다 ** - 그러려면 beforePiece.move( , )의 성공여부를
.move()의 응답값을 받아와 if 그 결과에 따라 실행시켜야한다. 특정 로직의 결과에 따라 움직인다면, 결과를 응답받지말고, 그 객체 text에 함형으로 넘겨주자
- **타 객체인
예시1: thr가능성있는 타객체.메세지() 이후의 로직들을 타객체메세지보낼때 같이 보내기
01 넘기고 싶은 로직을 () -> {}; 람다를 이용하여 함형을 만든다.
-
일단 넘기고 싶은 로직을
{}아웃풋 자리에 넣고 람다식()->{};을 만든다.() -> { this.value.put(afterPosition, beforePiece); this.value.put(beforePosition, new NullPiece(null)); }
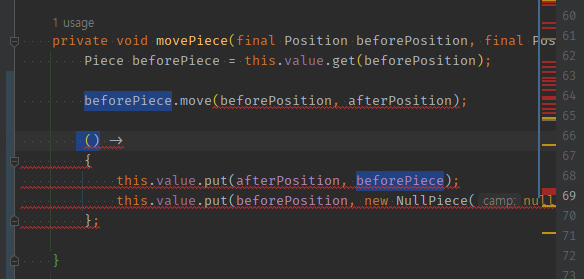
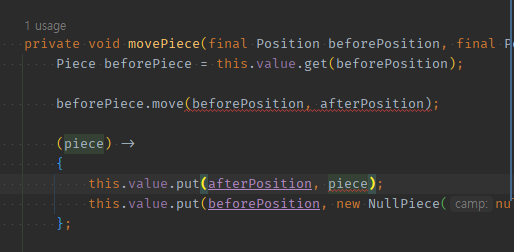
02 타 객체가 내부에 사용됬다면, 람다식의 (input) -> {};으로 받아 -> 함형.메서드( this );로 사용되도록 해야한다.
-
beforePiece.move(, )에 넘겨줄 예정이므로 piece를 함형 람다의 input으로 지정해주고, 고치자private void movePiece(final Position beforePosition, final Position afterPosition) { Piece beforePiece = this.value.get(beforePosition); beforePiece.move(beforePosition, afterPosition); (piece) -> { this.value.put(afterPosition, piece); this.value.put(beforePosition, new NullPiece(null)); }; }
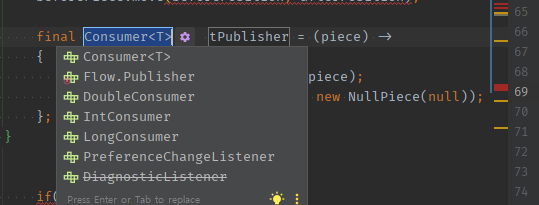
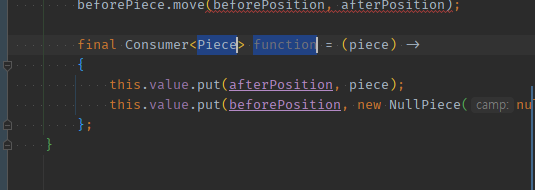
03 람다식의 input이 정해지면, [변수추출]로 함형종류 + inputType을 지정해준다 -> 변수추출하면 메서드 추출도 응답값 지정이 잘됨.
-
함형의
inputType에는넘겨받을 타 객체Piece로 정해줘야한다.private void movePiece(final Position beforePosition, final Position afterPosition) { Piece beforePiece = this.value.get(beforePosition); beforePiece.move(beforePosition, afterPosition); final Consumer<Piece> function = (piece) -> { this.value.put(afterPosition, piece); this.value.put(beforePosition, new NullPiece(null)); }; }
04 타 객체의 메서드(인자)로 넘겨주기 위해, 함형의 = 제외한 우항만 메서드 추출
-
추출할 메서드의 응답Type-> 타객체. 메서드(인자로 들어갈 Type)이 될 것이니 응답값이함수형 인터페이스가 되도록= 우항만 메서드 추출해준다.- 만약, 변수추출 안했다면 추론이 안되서 함형을 응답값으로 못빼주더라
-
=를 포함시켜서 추출하면 추출안됨.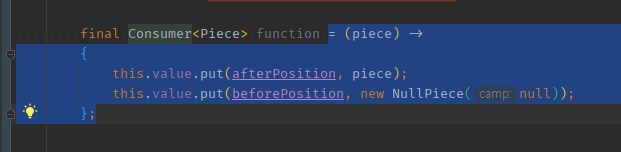
-
=제외시키고 함형 메서드추출하면 잘된다.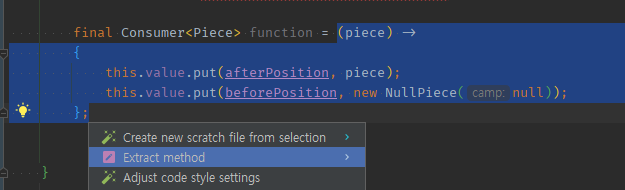
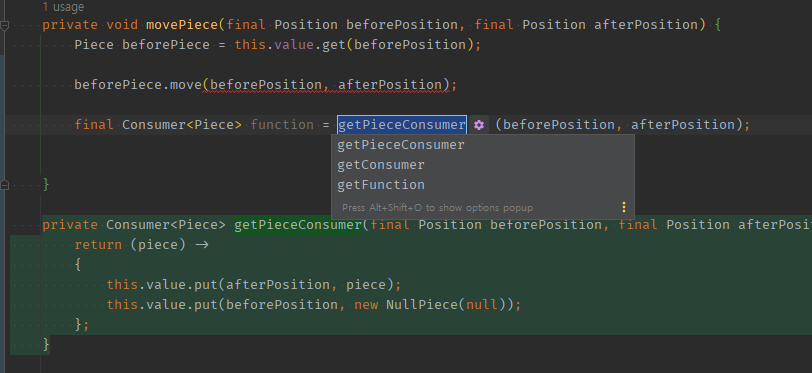
-
=을 제외하고우항만 메서드 추출해서, 응답값이 함수형 인터페이스로 잘 뽑히는지 확인한다.private void movePiece(final Position beforePosition, final Position afterPosition) { Piece beforePiece = this.value.get(beforePosition); beforePiece.move(beforePosition, afterPosition); final Consumer<Piece> function = getMoveConsumer(beforePosition, afterPosition); } private Consumer<Piece> getMoveConsumer(final Position beforePosition, final Position afterPosition) { return (piece) -> { this.value.put(afterPosition, piece); this.value.put(beforePosition, new NullPiece(null)); }; }
05 추출한 로직의 함형을, 타객체 메서드에 건네줘서 -> 내부에서 this를 사용해 실행되도록 옮긴다.
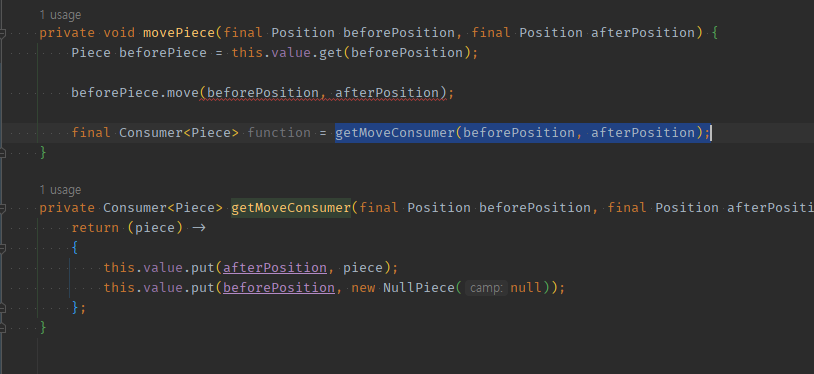
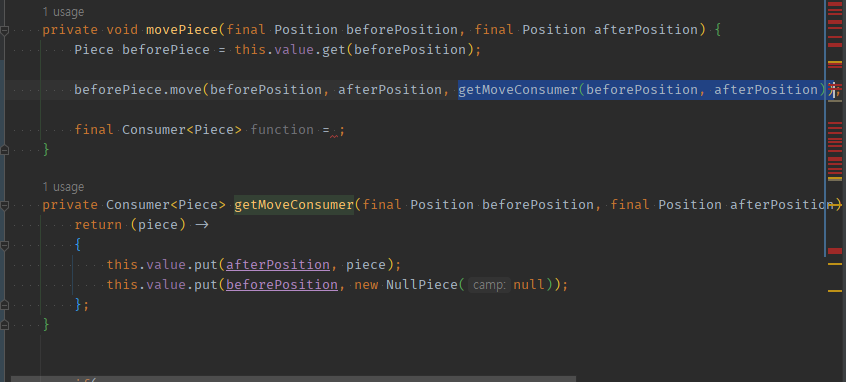
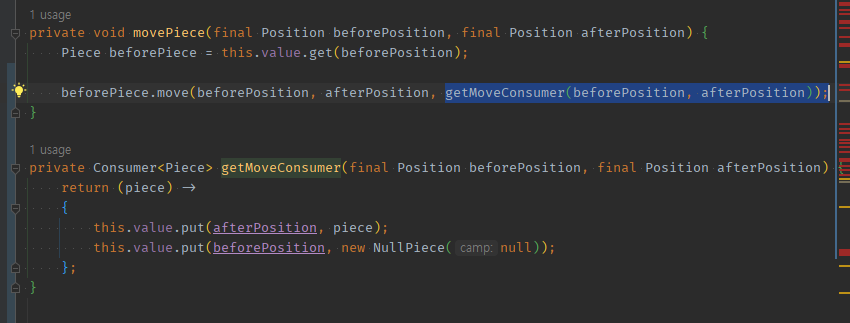
private void movePiece(final Position beforePosition, final Position afterPosition) {
Piece beforePiece = this.value.get(beforePosition);
beforePiece.move(beforePosition, afterPosition, getMoveConsumer(beforePosition, afterPosition));
}
06 함형으로 로직을 넘겨받은 타 객체는 내부에서 (this)를 인자로 주고 호출한다
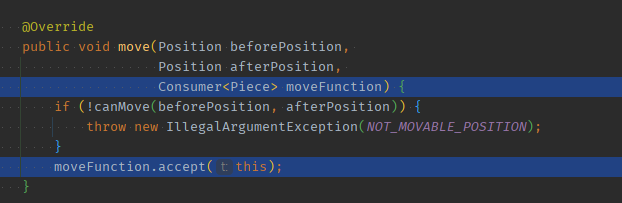
@Override
public void move(Position beforePosition,
Position afterPosition,
Consumer<Piece> moveFunction) {
if (!canMove(beforePosition, afterPosition)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(NOT_MOVABLE_POSITION);
}
moveFunction.accept(this);
}
예시2: 아래쪽 분기별 OutputView 로직이 도메인 샌드위치 사이에 위치한 경우 -> Runnable?객체면 Consumer?로 위쪽 도메인 메서드 인자에 함형메서드로 쏴서 넘겨주기
문제상황
public void run() {
OutputView.printStartMessage();
while (gameSwitch.isOn()) {
//도메인로직
final String command = InputView.inputCommand();
final GameCommand gameCommand = GameCommand.from(command);
gameCommand.execute(command, this);
//view로직 ( State에 따라서 출력 )
printBoardInfo();
//도메인로직2 (샌드위치유발) -> 특정상태인 경우, 다시 돌려주는 로직
if (state.isStatus()) {
state = state.toRunningState();
}
}
}
private void printBoardAndBeRunningIfStatus() {
if (isReadyOrRunning()) {
OutputView.printBoard(getBoard());
}
if (isStatusInRunning()) {
OutputView.printStatus(calculateStatus());
}
if (isFinishedAndGameEnd()) {
OutputView.printFinalStatus(calculateStatus());
}
}
01 view로직을 도메인 메서드 안에서 출력시키고 싶은데, view 사용 == view를 알면 안된다. -> view는 알면 안되지만, 함수형 인터페이스는 알아도 된다 -> view로직 전체 -> 람다를 통한 함형 -> 메서드추출후 응답에 함형
private Runnable printBoardInfo() {
return () -> {
if (isReadyOrRunning()) {
OutputView.printBoard(getBoard());
}
if (isStatusInRunning()) {
OutputView.printStatus(calculateStatus());
}
if (isFinishedAndGameEnd()) {
OutputView.printFinalStatus(calculateStatus());
}
};
}
02 도메인메서드의 인자에 함형 응답 메서드호출로 인한 함형인자를 추가하기
public void run() {
OutputView.printStartMessage();
while (gameSwitch.isOn()) {
final String command = InputView.inputCommand();
final GameCommand gameCommand = GameCommand.from(command);
gameCommand.execute(command, this, printBoardInfo());
//도메인로직2 (샌드위치유발) -> 특정상태인 경우, 다시 돌려주는 로직
if (state.isStatus()) {
state = state.toRunningState();
}
}
}
03 view로직을 함형으로 넘겨받은 도메인 메서드에서는 함형.메서드()로 가동시키기
- 함형으로 넘겨서 실행만 시키면
도메인은view를 모르고view로직이 담겨 실행직전인 함수형인터페이스만 알아도 된다.
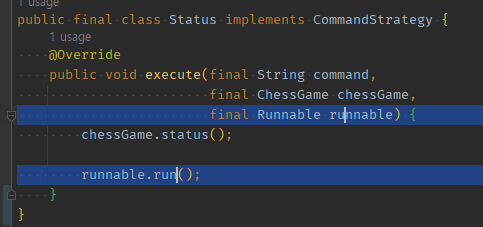
public final class Status implements CommandStrategy {
@Override
public void execute(final String command,
final ChessGame chessGame,
final Runnable runnable) {
chessGame.status();
runnable.run();
}
}
04 샌드위치를 만들던 도메인로직2도 해당분기에 맞게 도메인 내부로 옮겨준다.
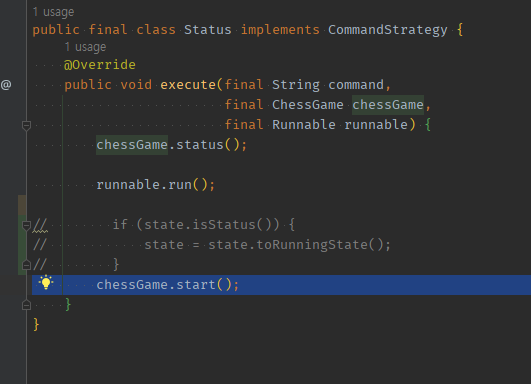
public final class Status implements CommandStrategy {
@Override
public void execute(final String command,
final ChessGame chessGame,
final Runnable runnable) {
chessGame.status();
runnable.run();
// if (state.isStatus()) {
// state = state.toRunningState();
// }
chessGame.start();
}
}
[람다식을 통한 함형]이 유용할 경우 3가지
list.sort( ) 속 [Comparator]의 역정렬 + thenComparing 2개이상 정렬
// 1
inventory.sort(Comparator.comparing(Apple::getWeight)
.reversed()); // 역으로 정렬
// 2
inventory.sort(Comparator.comparing(Apple::getWeight)
.reversed() // 역으로 정렬
.thenComparing(Apple::getCountry)); // 두 사과의 무게가 같으면 국가별로 정렬
참고) 그냥 Comparable안에서 2개 정렬
@Override
public int compareTo(Position o) {
return Comparator.comparing(Position::getRow, Comparator.reverseOrder())
.thenComparing(Position::getColumn)
.compare(this, o);
}
Predicate 1개에 .negate() 반전 이외에 .and( 람다 ) .or( 람다 )로 연쇄할 경우
Predicate<Apple> notRedApple = redApple.negate(); // 결과를 반전
Predicate<Apple> redAndHeavyApple = redApple
.and(apple -> apple.getWeight() > 150);
Predicate<Apple> redAndHeavyApple = redApple
.or(apple -> apple.getWeight() > 150);
Predicate<Apple> redAndHeavyAndGreenApple = redApple
.and(apple -> apple.getWeight() > 150)
.or(apple -> GREEN.equals(apple.getColor()));
// 빨간 사과 중 무게가 150 넘는 사과 혹은 초록 사과 (오른쪽 연결)
수식용 Function 들을 여러개 만들어놓고 .andThen( ) or .compose( )로 조합
compose( )는 뒤에 람다부터계산
Function<Integer, Integer> plus10 = (number) -> number + 10;
Function<Integer, Integer> multiply3 = (number) -> number * 3;
Function<Integer, Integer> multiply3AndPlus10 = plus10.compose(multiply3);
System.out.println(multiply3AndPlus10.apply(4)); // 결과 22
Function<Integer, Integer> plus10AndMultiply3 = plus10.andThen(multiply3);
System.out.println(plus10AndMultiply3.apply(4); // 결과 42