클린아키텍쳐 05 ManyEntity Register Controller와 test
python clean architecture
📜 제목으로 보기
- 클린 아키텍쳐 5장
- 1 ManyEntity Register Controller - register_pet_controller
- 01 ManyEntity register controller의 필수params들 검증 ~ usecase method 호출까지
- controller는 usecase를 인자로 받아야하니, use case interface import해서 생성자 작성
- controller는 handle method를 가지며, HttpRequest가 input으로 HttpResponse가 output으로
- controller도 usecase처럼 if 조건만족시 성공의 response = None으로 시작하지만, validate_entry(Type검사) 대신 if http_request.요구필드(필수필드 존재검사)로 validate한다.
- body_params에는 [nullable(age)를 제외하고] 생성에 필요한 필수 필드들(id제외, nullable제외)이 in으로 keys()에 들어가있어야 하니, if로 검사한다.
- select의 query_params는 선택형인자들로서 if문으로 잇고/없고를 모든 경우를 나눴지만, insert의 body_params는 and로 생성에 필수 필드들은 무조건 and로 다있어야한다. 대신 nullable=True의 age필드는 검사항목에서 제외한다. fk필드의 경우, request에서 애초에 fk_information의 dict로 들어와야한다.
- fk정보는 select를 위한 정보만 dict로 들어와서, PK usecase에서 private메서드로 탐색하여 validate한다. 각각의 repo/usecase(필드별개별) method에서는 fk_id or fk_unique필드만 사용하지만, [PK usecase으로는 fk_information의 dict형태]로 묶여서 들어와야한다
- fk_information(dict)에도 select를 위한 선택형인자 pk or unqiuekey 둘중에 1개라도 포함하고 있는지 in keys()를 통해 확인한다.
- request.body 생성필수 필드들 및 fk select필수필드 존재 검증이 ififif로 끝났다면, [nullable필드]를 확인하고 있으면 받고, 없어도 None으로 받아놔야, use case method에 인자로 넣어줄 수 있다.
- 존재 검증 만족시, 모든 필드들을 지역변수로 뽑은 다음 usecase method에 넣어서 호출한다
- 02 ManyEntity register controller의 usecase method response에 대한 ififif존재검증들마다 elseelseelse HttpReponse return 처리
- fk_information의 필수필드 존재검증 실패(else) -> usecase Dict[bool, List[DTO]]의 실패처리한다.
- body 속 필수 필드 존재검증 실패(else)시에도 usecase 실패 response를 작성한다.
- if if 성공usecase응답에 대한 else: 가상 실패응답 else: 가상 실패응답 까지 다 처리하고 나서 => 성공response인지 vs실패response인지 확인한다.
- usecase실패응답에 대한 HttpReponse를 early return후, 성공을 200 + Data로 return한다
- 03 생성에 필요한 body가 자체가 없는 경우, 조회시필요한 query가 없는 것과 마찬가지로 400에러
- 01 ManyEntity register controller의 필수params들 검증 ~ usecase method 호출까지
- 2 ManyEntity Register Controller test - register_pet_controller_test.py
- 01 src>presenter>controllers> register_pet_controller_test.py를 생성
- 02 src>data>test폴더에 > register_pet_spy.py 만들어서 정의
- 03 문제는 fk_information dict를 http_request로부터 받아서, FindFk usecase를 처리하는 private메서드를 처리하는 것이다.
- 04 이제 controller test를 작성시작한다.
- 05 Controller의 handle method로 오는 input은 HttpRequest(usecase test시 오는 attributes를 감싼)
- 06 handle method에 input으로 HttpRequest객체로 주고 response지역변수에 HttpResponse를 받는다.
- 07 Input Test
- 08 Output Test
- 3 ManyEntity Register Controller Fail Test
- 참고
- 1 ManyEntity Register Controller - register_pet_controller
클린 아키텍쳐 5장
1 ManyEntity Register Controller - register_pet_controller
01 ManyEntity register controller의 필수params들 검증 ~ usecase method 호출까지
-
register_pet_controller.py를 만들고 작성한다.
controller는 usecase를 인자로 받아야하니, use case interface import해서 생성자 작성
from typing import Type
from src.domain.use_cases import RegisterPet
class RegisterPetController:
""" Class to define controller to register_pet use case """
def __init__(self, register_pet_use_case: Type[RegisterPet]) -> None:
self.register_pet_use_case = register_pet_use_case
controller는 handle method를 가지며, HttpRequest가 input으로 HttpResponse가 output으로
from typing import Type
from src.domain.use_cases import RegisterPet
from src.presenters.helpers import HttpRequest
from src.presenters.helpers import HttpResponse
class RegisterPetController:
""" Class to define controller to register_pet use case """
def __init__(self, register_pet_use_case: Type[RegisterPet]) -> None:
self.register_pet_use_case = register_pet_use_case
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
controller도 usecase처럼 if 조건만족시 성공의 response = None으로 시작하지만, validate_entry(Type검사) 대신 if http_request.요구필드(필수필드 존재검사)로 validate한다.
find(select)는 .query를 뒤져 validte하지만, register(insert)는 .body를 뒤져 validate한다!! body에 pet생성필드가 다 있어야한다
class RegisterPetController:
""" Class to define controller to register_pet use case """
def __init__(self, register_pet_use_case: Type[RegisterPet]) -> None:
self.register_pet_use_case = register_pet_use_case
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
response = None
if http_request.body:
# if body in http_request
body_params에는 [nullable(age)를 제외하고] 생성에 필요한 필수 필드들(id제외, nullable제외)이 in으로 keys()에 들어가있어야 하니, if로 검사한다.
select의 query_params는 선택형인자들로서 if문으로 잇고/없고를 모든 경우를 나눴지만, insert의 body_params는 and로 생성에 필수 필드들은 무조건 and로 다있어야한다. 대신 nullable=True의 age필드는 검사항목에서 제외한다. fk필드의 경우, request에서 애초에 fk_information의 dict로 들어와야한다.
fk정보는 select를 위한 정보만 dict로 들어와서, PK usecase에서 private메서드로 탐색하여 validate한다. 각각의 repo/usecase(필드별개별) method에서는 fk_id or fk_unique필드만 사용하지만, [PK usecase으로는 fk_information의 dict형태]로 묶여서 들어와야한다
class RegisterPetController:
#...
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
response = None
if http_request.body:
# if body in http_request
body_params = http_request.body.keys()
if "name" in body_params and "specie" in body_params and "user_information" in body_params:
fk_information(dict)에도 select를 위한 선택형인자 pk or unqiuekey 둘중에 1개라도 포함하고 있는지 in keys()를 통해 확인한다.
class RegisterPetController:
#...
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
response = None
if http_request.body:
# if body in http_request
body_params = http_request.body.keys()
if "name" in body_params and "specie" in body_params and "user_information" in body_params:
user_information_params = http_request.body["user_information"].keys()
if "user_id" in user_information_params or "user_name" in user_information_params:
request.body 생성필수 필드들 및 fk select필수필드 존재 검증이 ififif로 끝났다면, [nullable필드]를 확인하고 있으면 받고, 없어도 None으로 받아놔야, use case method에 인자로 넣어줄 수 있다.
usecase register method에서 nullable필드는 선택형으로 맨 마지막에 = None으로 넣어줬지만, [안에 있는지 없는지 모르는 상황]에서는 확인하고 변수로 받아서 넣어준다.
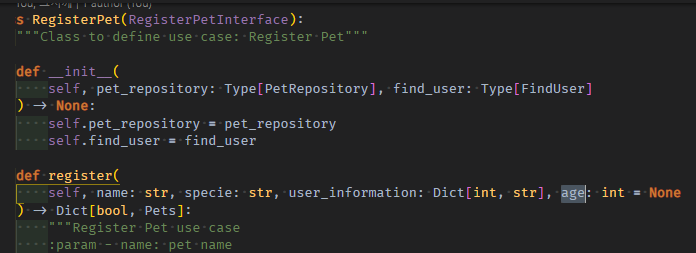
class RegisterPetController:
#...
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
#...
response = None
if http_request.body:
body_params = http_request.body.keys()
if "name" in body_params and "specie" in body_params and "user_information" in body_params:
user_information_params = http_request.body["user_information"].keys()
if "user_id" in user_information_params or "user_name" in user_information_params:
name = http_request.body["name"]
specie = http_request.body["specie"]
user_information = http_request.body["user_information"]
if "age" in body_params:
age = http_request.body["age"]
else:
age = None
존재 검증 만족시, 모든 필드들을 지역변수로 뽑은 다음 usecase method에 넣어서 호출한다
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
response = None
if http_request.body:
# if body in http_request
body_params = http_request.body.keys()
if "name" in body_params and "specie" in body_params and "user_information" in body_params:
user_information_params = http_request.body["user_information"].keys()
if "user_id" in user_information_params or "user_name" in user_information_params:
name = http_request.body["name"]
specie = http_request.body["specie"]
user_information = http_request.body["user_information"]
if "age" in body_params:
age = http_request.body["age"]
else:
age = None
response = self.register_pet_use_case.register(
name=name,
specie=specie,
user_information=user_information,
age=age
)
02 ManyEntity register controller의 usecase method response에 대한 ififif존재검증들마다 elseelseelse HttpReponse return 처리
fk_information의 필수필드 존재검증 실패(else) -> usecase Dict[bool, List[DTO]]의 실패처리한다.
controller의 return은 HttpResponse지만, 일단 usecase의 성공에 대한 response부터 만들고, if usecase_reponse[“Success”] is False로 가야한다
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
response = None
if http_request.body:
# if body in http_request
body_params = http_request.body.keys()
if "name" in body_params and "specie" in body_params and "user_information" in body_params:
user_information_params = http_request.body["user_information"].keys()
if "user_id" in user_information_params or "user_name" in user_information_params:
name = http_request.body["name"]
specie = http_request.body["specie"]
user_information = http_request.body["user_information"]
if "age" in body_params:
age = http_request.body["age"]
else:
age = None
response = self.register_pet_use_case.register(
name=name,
specie=specie,
user_information=user_information,
age=age
)
else:
response = {"Success": False, "Data": None}
body 속 필수 필드 존재검증 실패(else)시에도 usecase 실패 response를 작성한다.
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
response = None
if http_request.body:
# if body in http_request
body_params = http_request.body.keys()
if "name" in body_params and "specie" in body_params and "user_information" in body_params:
user_information_params = http_request.body["user_information"].keys()
if "user_id" in user_information_params or "user_name" in user_information_params:
name = http_request.body["name"]
specie = http_request.body["specie"]
user_information = http_request.body["user_information"]
if "age" in body_params:
age = http_request.body["age"]
else:
age = None
response = self.register_pet_use_case.register(
name=name,
specie=specie,
user_information=user_information,
age=age
)
else:
response = {"Success": False, "Data": None}
else:
response = {"Success": False, "Data": None}
if if 성공usecase응답에 대한 else: 가상 실패응답 else: 가상 실패응답 까지 다 처리하고 나서 => 성공response인지 vs실패response인지 확인한다.
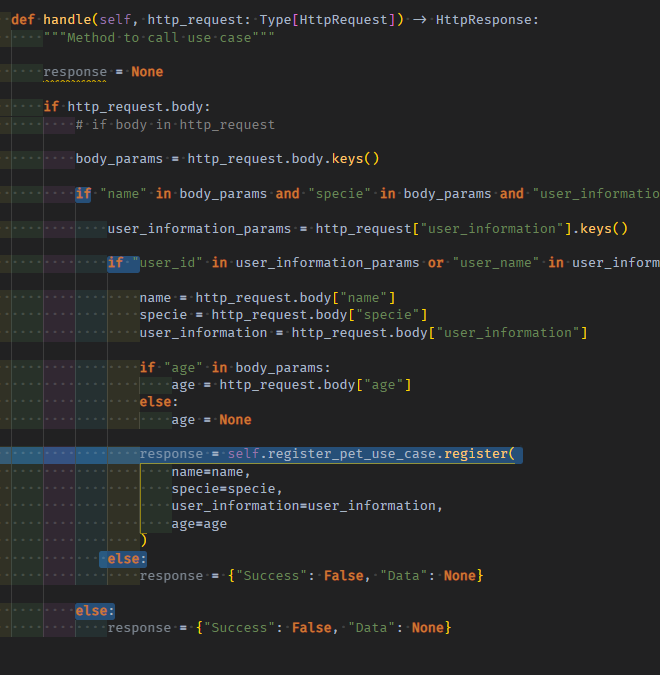
if 성공/실패 중 실패면, HttpResponse를 실패로 만들어 early return한다. 인자
-
422: 필수param(dict속 필드)이 빠졌을 경우(존재검증) or 필수param이 validate_entry실패할 경우
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
response = None
if http_request.body:
# if body in http_request
body_params = http_request.body.keys()
if "name" in body_params and "specie" in body_params and "user_information" in body_params:
user_information_params = http_request.body["user_information"].keys()
if "user_id" in user_information_params or "user_name" in user_information_params:
name = http_request.body["name"]
specie = http_request.body["specie"]
user_information = http_request.body["user_information"]
if "age" in body_params:
age = http_request.body["age"]
else:
age = None
response = self.register_pet_use_case.register(
name=name,
specie=specie,
user_information=user_information,
age=age
)
else:
response = {"Success": False, "Data": None}
else:
response = {"Success": False, "Data": None}
if response["Success"] is False:
http_error = HttpErrors.error_422()
return HttpResponse(status_code=http_error["status_code"], body=http_error["body"])
usecase실패응답에 대한 HttpReponse를 early return후, 성공을 200 + Data로 return한다
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
response = None
if http_request.body:
# if body in http_request
body_params = http_request.body.keys()
if "name" in body_params and "specie" in body_params and "user_information" in body_params:
user_information_params = http_request.body["user_information"].keys()
if "user_id" in user_information_params or "user_name" in user_information_params:
name = http_request.body["name"]
specie = http_request.body["specie"]
user_information = http_request.body["user_information"]
if "age" in body_params:
age = http_request.body["age"]
else:
age = None
response = self.register_pet_use_case.register(
name=name,
specie=specie,
user_information=user_information,
age=age
)
else:
response = {"Success": False, "Data": None}
else:
response = {"Success": False, "Data": None}
if response["Success"] is False:
http_error = HttpErrors.error_422()
return HttpResponse(status_code=http_error["status_code"], body=http_error["body"])
return HttpResponse(status_code=200, body=response["Data"])
03 생성에 필요한 body가 자체가 없는 경우, 조회시필요한 query가 없는 것과 마찬가지로 400에러
- if http_request.body: 에 대한 else:시 return
def handle(self, http_request: Type[HttpRequest]) -> HttpResponse:
"""Method to call use case"""
response = None
if http_request.body:
# if body in http_request
body_params = http_request.body.keys()
if "name" in body_params and "specie" in body_params and "user_information" in body_params:
user_information_params = http_request.body["user_information"].keys()
if "user_id" in user_information_params or "user_name" in user_information_params:
name = http_request.body["name"]
specie = http_request.body["specie"]
user_information = http_request.body["user_information"]
if "age" in body_params:
age = http_request.body["age"]
else:
age = None
response = self.register_pet_use_case.register(
name=name,
specie=specie,
user_information=user_information,
age=age
)
else:
response = {"Success": False, "Data": None}
else:
response = {"Success": False, "Data": None}
if response["Success"] is False:
http_error = HttpErrors.error_422()
return HttpResponse(status_code=http_error["status_code"], body=http_error["body"])
return HttpResponse(status_code=200, body=response["Data"])
http_error =HttpErrors.error_400()
return HttpResponse(status_code=http_error["status_code"], body=http_error["body"])
2 ManyEntity Register Controller test - register_pet_controller_test.py
01 src>presenter>controllers> register_pet_controller_test.py를 생성
controller는 repo를 품는 UseCase를 품어서 생성되니, Usecase Spy부터 만들고 오자
02 src>data>test폴더에 > register_pet_spy.py 만들어서 정의
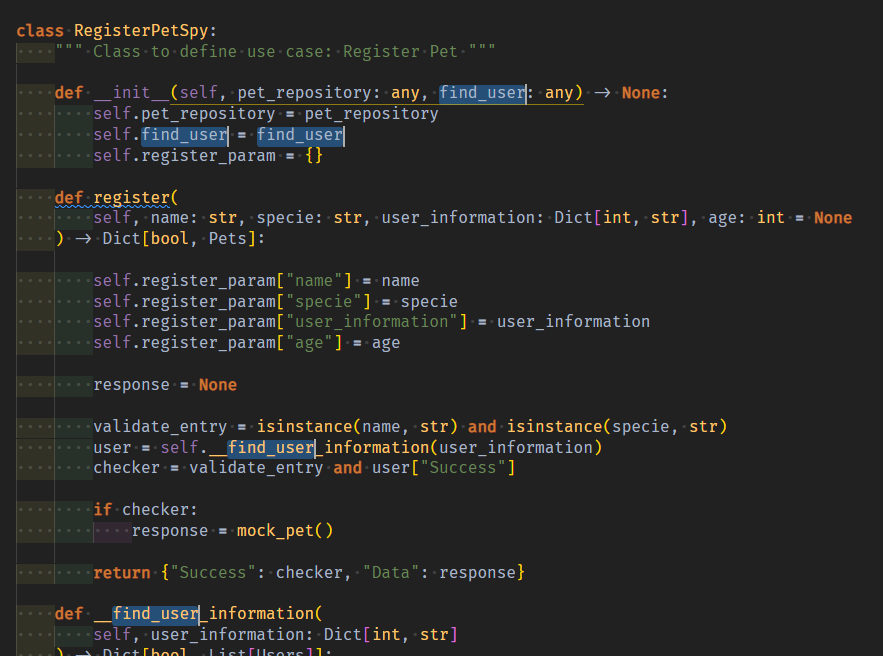
class RegisterPetSpy:
""" Class to define use case: Register Pet """
spy를 정의할 땐, 원본을 같이 보면서 정의하자
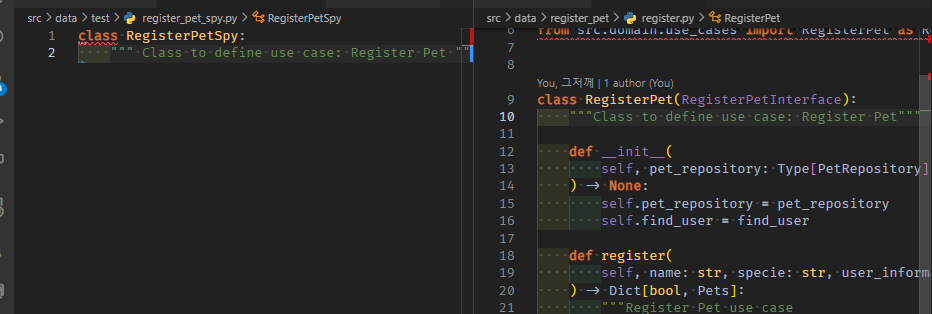
생성자를 복사해오되, 실제repo/실제Fk usecase 대신 Type없는 repoSpy/usecaseSpy가 들어갈 것이므로 둘다, 파라미터 타입을 any로 바꾼다.
class RegisterPetSpy:
""" Class to define use case: Register Pet """
def __init__(self, pet_repository: any, find_user: any) -> None:
self.pet_repository = pet_repository
self.find_user = find_user
Spy는 repo든 usecase든, method input을 품을 param_dict를 생성자에 추가한다
class RegisterPetSpy:
""" Class to define use case: Register Pet """
def __init__(self, pet_repository: any, find_user: any) -> None:
self.pet_repository = pet_repository
self.find_user = find_user
self.register_param = {}
usecase 원본 method도 복사해와서 수정한다.
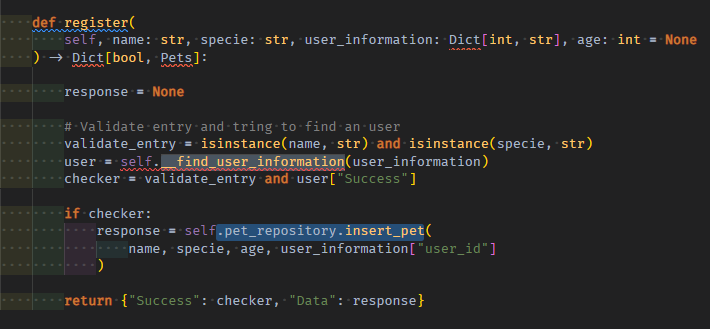
내부 구현부 중에서 repo의 insert_pet method를 호출해서 응답받는 중간 output은 mock_pet로 대체한다
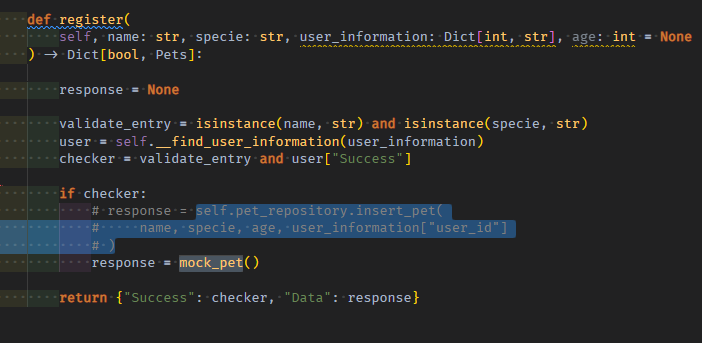
class RegisterPetSpy:
""" Class to define use case: Register Pet """
def __init__(self, pet_repository: any, find_user: any) -> None:
self.pet_repository = pet_repository
self.find_user = find_user
self.register_param = {}
def register(
self, name: str, specie: str, user_information: Dict[int, str], age: int = None
) -> Dict[bool, Pets]:
response = None
validate_entry = isinstance(name, str) and isinstance(specie, str)
user = self.__find_user_information(user_information)
checker = validate_entry and user["Success"]
if checker:
response = mock_pet()
return {"Success": checker, "Data": response}
method의 input들은 self. method_param dict에 보관한다
def register(
self, name: str, specie: str, user_information: Dict[int, str], age: int = None
) -> Dict[bool, Pets]:
self.register_param["name"] = name
self.register_param["specie"] = specie
self.register_param["user_information"] = user_information
self.register_param["age"] = age
03 문제는 fk_information dict를 http_request로부터 받아서, FindFk usecase를 처리하는 private메서드를 처리하는 것이다.
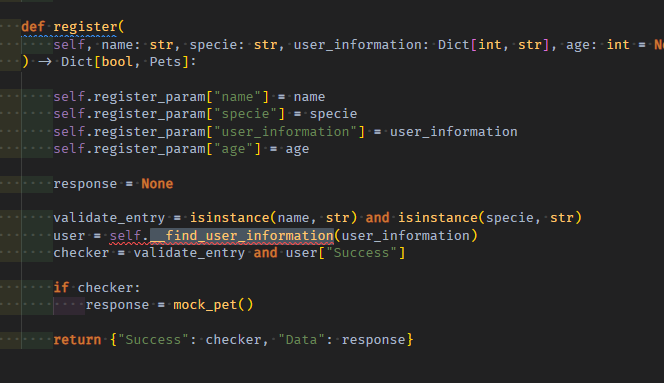
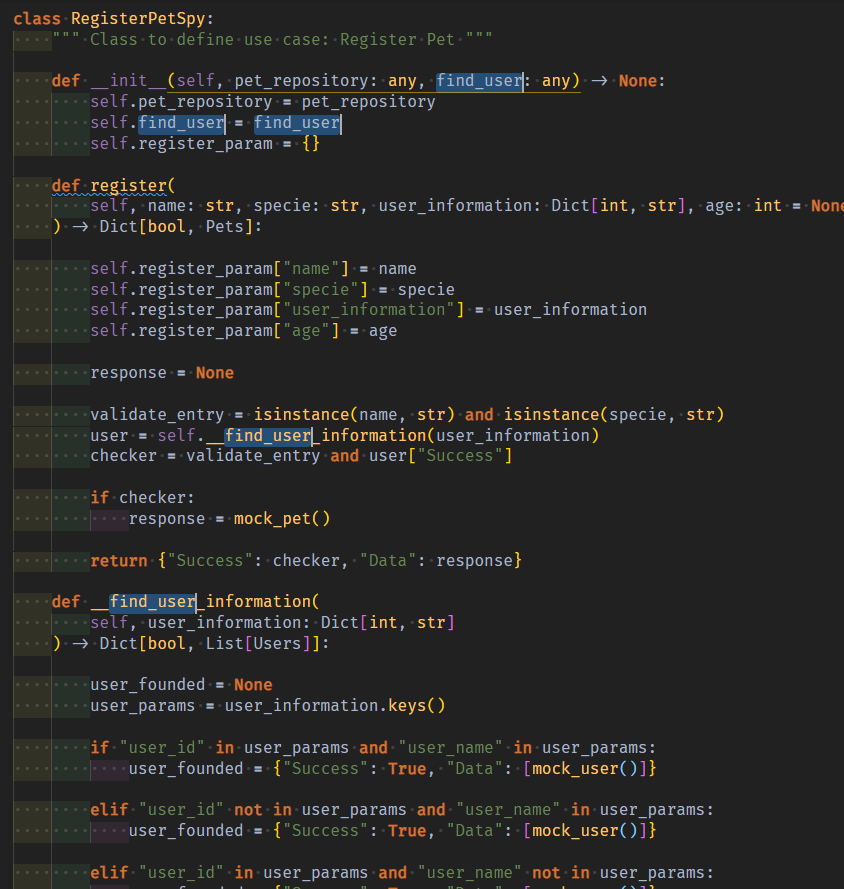
user_information에 대한 validate는 원본 속 private메서드에서 한것 처럼 진행되어야하니, private메서드도 가져온다(spy는 input을 품고잇지만, 사용은 안할뿐이지 검증은 원본과 같이 그대로 진행한다.)
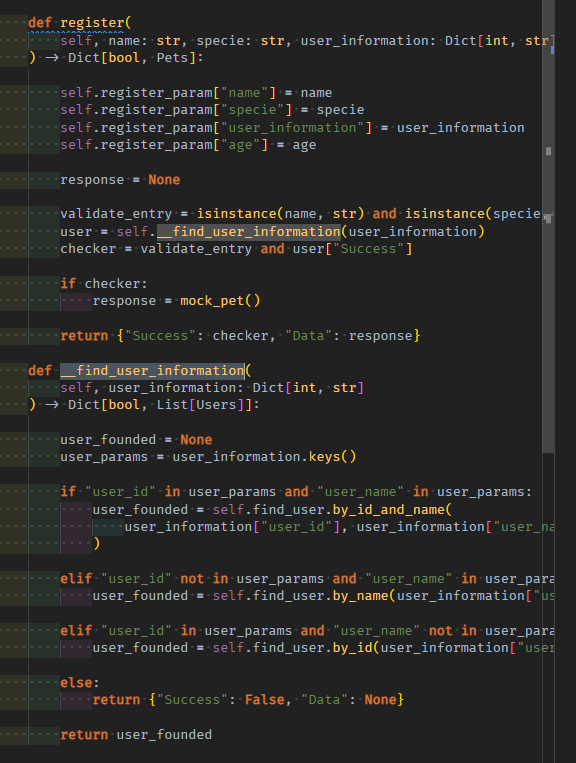
이번엔 fk의 usecase method를 호출을 통한 중간output을 Dict[bool, List[DTO]] 형태로 mock_users()객체와 함께 만들어낸다.
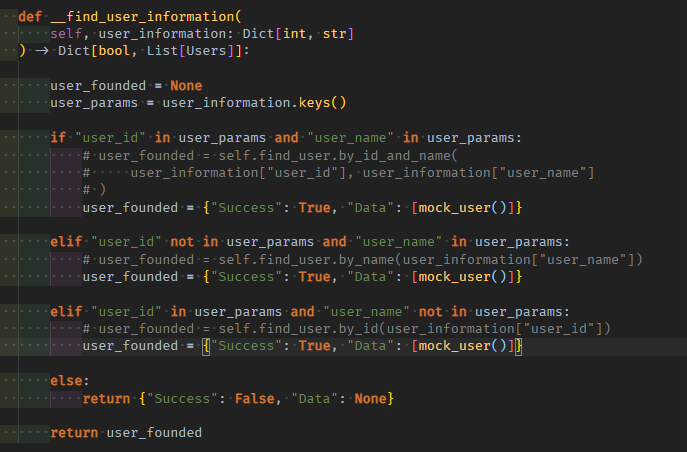
class RegisterPetSpy:
""" Class to define use case: Register Pet """
def __init__(self, pet_repository: any, find_user: any) -> None:
self.pet_repository = pet_repository
self.find_user = find_user
self.register_param = {}
def register(
self, name: str, specie: str, user_information: Dict[int, str], age: int = None
) -> Dict[bool, Pets]:
self.register_param["name"] = name
self.register_param["specie"] = specie
self.register_param["user_information"] = user_information
self.register_param["age"] = age
response = None
validate_entry = isinstance(name, str) and isinstance(specie, str)
user = self.__find_user_information(user_information)
checker = validate_entry and user["Success"]
if checker:
response = mock_pet()
return {"Success": checker, "Data": response}
def __find_user_information(
self, user_information: Dict[int, str]
) -> Dict[bool, List[Users]]:
user_founded = None
user_params = user_information.keys()
if "user_id" in user_params and "user_name" in user_params:
user_founded = {"Success": True, "Data": [mock_user()]}
elif "user_id" not in user_params and "user_name" in user_params:
user_founded = {"Success": True, "Data": [mock_user()]}
elif "user_id" in user_params and "user_name" not in user_params:
user_founded = {"Success": True, "Data": [mock_user()]}
else:
return {"Success": False, "Data": None}
return user_founded
- 완성됬으니 init에 올린다.
from .find_user_spy import FindUserSpy
from .register_pet_spy import RegisterPetSpy
04 이제 controller test를 작성시작한다.
- faker + test할 controller class + 인자에 들어갈 usecase Spy import
from faker import Faker
from .register_pet_controller import RegisterPetController
from src.data.test import RegisterPetSpy
인자에 들어갈 Spy가 UseCase면, 그놈이 품고 태어나야할 RepoSpy도 같이 import하자
만일 ManyEntity register UseCaseSpy면,자신의 RepoSpy외, FindFkUseCaseSpy도 동시에 품어서 생성해야하고, 이어서 FkRepoSpy도 필요하다
- UseCaseSpy
- RepoSpy (+ FkUseCaseSpy -> +FkRepoSpy)
from faker import Faker
from .register_pet_controller import RegisterPetController
from src.data.test import RegisterPetSpy, FindUserSpy
from src.infra.test import PetRepositorySpy, UserRepositorySpy
faker = Faker()
test_handle메서드에서는 controller객체를 생성하기 위해, useacse -> repospy 먼저 생성해서 넣어준다
from faker import Faker
from .register_pet_controller import RegisterPetController
from src.data.test import RegisterPetSpy, FindUserSpy
from src.infra.test import PetRepositorySpy, UserRepositorySpy
faker = Faker()
def test_handle():
"""Testing Handle method"""
register_use_case = RegisterPetSpy(PetRepositorySpy(), FindUserSpy(UserRepositorySpy()))
사실, ManyEntityUsecase Spy에서는 FindFk usecase가 필요없다 -> Spy가 아니라면, private메서드 내에서 FindUser를 호출하는데, Spy에서는 output을 대체하기 때문이다.
-
RegisterPet: FindFk Usecase가 private메서드에서 중간output을 받기위해 사용된다.
-
RegisterPetSpy: FindFk UseCaseSpy는 사용되질 private메서드에서 호출에 사용되지 않는다.
RegisterManyEntity의 Spy생성에서는 FindFk Usecase를 None으로 대체한다(사용안되서)
from faker import Faker
from .register_pet_controller import RegisterPetController
from src.data.test import RegisterPetSpy, FindUserSpy
from src.infra.test import PetRepositorySpy, UserRepositorySpy
faker = Faker()
def test_handle():
""" Testing Handle method"""
# register_use_case = RegisterPetSpy(PetRepositorySpy(), FindUserSpy(UserRepositorySpy()))
register_use_case = RegisterPetSpy(PetRepositorySpy(), None)
- controller 객체를 생성한다.
def test_handle():
""" Testing Handle method"""
# register_use_case = RegisterPetSpy(PetRepositorySpy(), FindUserSpy(UserRepositorySpy()))
register_use_case = RegisterPetSpy(PetRepositorySpy(), None)
register_pet_controller = RegisterPetController(register_use_case)
05 Controller의 handle method로 오는 input은 HttpRequest(usecase test시 오는 attributes를 감싼)
controller handle method test시, Find/select계열의 GET 요청이라면, body없이 query만 오므로 HttpRequest객체 생성시 간단하게 바로 넣었다.
- find_user_controller_test.py
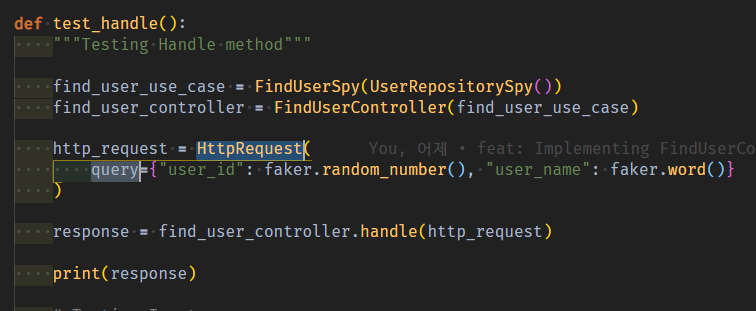
register/insert 계열의 POST 요청은 객체생성에 필요한 모든 정보가 body에 담겨져서 오니, attributes로 먼저 body를 채울 정보를 만들고 -> body를 채운 HttpRequest객체를 만들어서 input으로 준다.
-
specie는 enum에 정해놓은 문자열 중 1개를 줘야한다.
def test_handle():
""" Testing Handle method"""
register_use_case = RegisterPetSpy(PetRepositorySpy(), None)
register_pet_controller = RegisterPetController(register_use_case)
attributes = {
"name": faker.word(),
"specie": "dog",
"age": faker.random_number(),
"user_information": {
"user_id": faker.random_number(),
"user_name": faker.word(),
}
}
06 handle method에 input으로 HttpRequest객체로 주고 response지역변수에 HttpResponse를 받는다.
body채우기용 attributes변수도 있지만, input test에서 Spy_method_param_dict vs http_requeste.body[”“]로 잘먹엇는지 input객체로 확인하기 위해서, http_request 변수도 따로 받아준다.
def test_handle():
""" Testing Handle method"""
register_use_case = RegisterPetSpy(PetRepositorySpy(), None)
register_pet_controller = RegisterPetController(register_use_case)
attributes = {
"name": faker.word(),
"specie": "Dog",
"age": faker.random_number(),
"user_information": {
"user_id": faker.random_number(),
"user_name": faker.word(),
}
}
http_request = HttpRequest(body=attributes)
response = register_pet_controller.handle(HttpRequest(body=attributes))
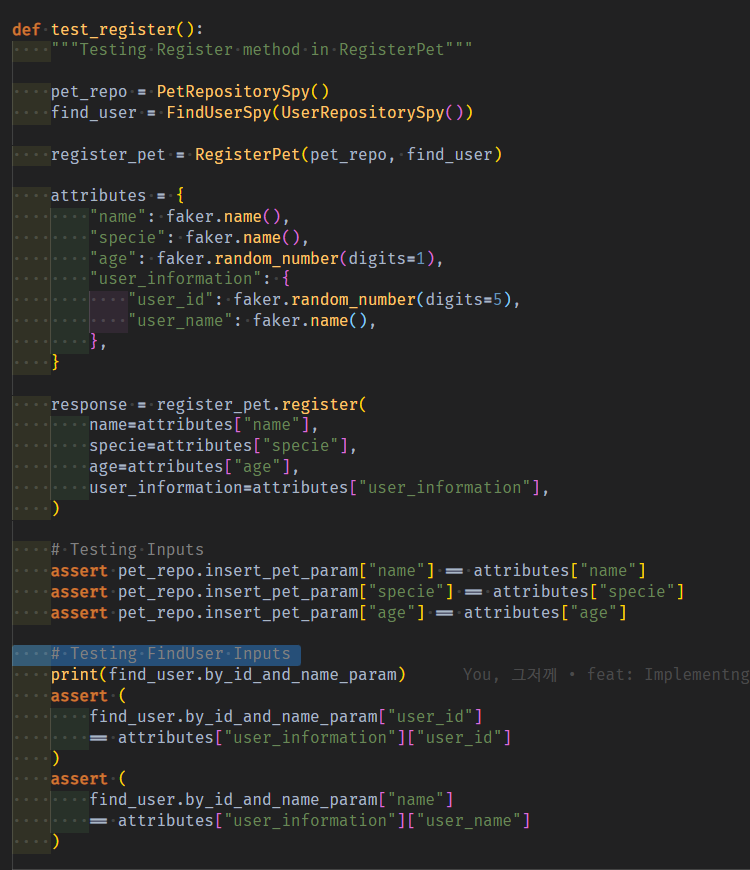
07 Input Test
input 테스트는 Spy객체가 param dict에 HttpRequest객체 속 .body필드(GET이면 .query) 속 attributes필드를 잘 먹었는지 확인한다.
fk_information 정보는, Controller가 아닌 Usecase 레벨의 test라면, private메서드에서 FindFk usecase Spy객체가 먹고 있기 때문에, Testing inputs에서 바로 확인 안했었다. 하지만, Controller test에선 FindFk usecase Spy조차 도입안하기 때문에, 바로 검사해버린다.
-
참고: UseCase에서는 fk_information 정보를 자기가 먹지 않고, private메서드에서 , Fk Usecase에게 넘겨서 먹이고, 따로 검사한다.
def test_handle():
""" Testing Handle method"""
register_use_case = RegisterPetSpy(PetRepositorySpy(), None)
register_pet_controller = RegisterPetController(register_use_case)
attributes = {
"name": faker.word(),
"specie": "Dog",
"age": faker.random_number(),
"user_information": {
"user_id": faker.random_number(),
"user_name": faker.word(),
}
}
http_request = HttpRequest(body=attributes)
response = register_pet_controller.handle(http_request)
print(response)
# Testing inputs
assert register_use_case.register_param["name"] == http_request.body["name"]
assert register_use_case.register_param["specie"] == http_request.body["specie"]
assert register_use_case.register_param["user_information"] == http_request.body["user_information"]
assert register_use_case.register_param["age"] == http_request.body["age"]
pytest 돌릴 때, -vs주는 이유는 print(response)도 찍어서 같이보기 위해~!
HttpResponse (status_code=200, body=Pets(id=68452, name='Kristen Sutton', specie='dog', age=1, user_id=58342))
08 Output Test
controller의 output test는 response가 status_code=와 body로 구성되어있으니, 200인지 / body dict에 “error” key가 안꼽혀있는지 not in 으로 확인한다.
# Testing Outputs
assert response.status_code == 200
assert "error" not in response.body
- pytest
3 ManyEntity Register Controller Fail Test
controller fail test는 일단, handle의 어느 지점(else)의 에러를 낼지 부터 살펴봐야한다.
생략하고 커밋
git status
git add .
git commit -am "feat: Implementing RegisterPetController"
git commit -am "feat: Implementing RegisterPetController"
참고
gitignore
-
git에 commit되었던 것을 ignore하고 싶을 때
git rm [파일명] --cached -
git amend
git commit --amend --no-edit
- console 등에서 init import부터 생기는 pycache폴더
- venv
- 연습용 sqlite .db파일
- pytest시 생기는 .pytest_cache 폴더
**/__pycache__
venv
storage.db
.pytest_cache
sqlalchemy패키지
- 일반 패키지: create_engine / 칼럼재료들
- .orm 패키지:
- relatioship: 1:M에서 1에 해당하는 table이 들고 있는 가짜칼럼
- sessionmaker: handler class 속 enter에서 engine을 묶어서 session을 반환해주는 놈
- 계층별 변수정리
- id : sqlalchemy -> repo부터는 fk_id도 있으니
pk_id - name: sqlalchemy->repo->usecase까지는 그냥 name (선택인자 개별메서드에by_name)-> controller부터는 외부에선 다른(pet)_name도 있으니
pk_name
- id : sqlalchemy -> repo부터는 fk_id도 있으니
github에서 br따서 작업하기
[1-1] github에서 br생성 ~ clone
-
github에 들어가서
feat/~로 브랜치 생성 -
해당 br만 clone
git clone -b [branch] [git주소]
clone후 초기 작업 세팅
- gitignore중에 db파일 있으면 옮겨주기
- 없으면 config import해서 Base + handler -> get_enigne -> bind한 다음, create_all()해줘야할듯??
- github에서 따온 빈 새br에 대해, venv를 만들고 활성화하고 vscode를 연다
python -m virtualenv -p python310 venv
.\venv\Scripts\activate
- 최초 requirements.txt 직접 설치
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
- 최초 pre-commit install 직접 세팅
pre-commit install
- vscode 열고 interpreter venv로 지정
code .
[1-2] 작업끝난 br의 폴더에서 새 작업 br생성 ~ 분기게시 (초기세팅 또 안해도 되는 장점)
-
현재 br를 확인한다.
git branch * feat/register_user_use_case -
checkout -b로 새 br 생성하여 진입하기
- 원래는 github에서 create branch했었음.
git checkout -b feat/generic_use_cases git branch * feat/generic_use_cases feat/register_user_use_case -
git push -u origin [branch명]으로
새로생성한 br를 push해서 github에 생성하기- vscode에서는 push -u origin [branch] 대신
분기게시가 뜬다.
- vscode에서는 push -u origin [branch] 대신
-
github에서 빈 분기가 생성되었는지 확인하기
- github에 merge되기 위해서는 직전 작업이후
github에 새 작업 br를 먼저 생성해놓고 작업에 들어가야한다
- github에 merge되기 위해서는 직전 작업이후
[1-3] 옛날에 따둔 br에서 작업시작할 땐, 최신 master를 rebase후에 작업시작하기
-
git checkout master를 통해 안가져와서 안보이던 master를 만든다- -b의 새로만든 것이 아니므로 remote와 연결된 master가 된다.
-
git branch로 확인
git checkout master git branch -
git pull로 master에 최신 코드를 가져온다git pull -
rebase받을 업뎃안된 작업br로 넘어간 뒤,
matser의 내용을 rebase로 받아온다git checkout [작업br] git rebase master git log --oneline
[2] 해당br 작업(테스트) 완료후 ~ merge까지 정리
-
status 확인후 add . 후 -am으로 커밋->실패->-am커밋
- add를 먼저 날려야 add된상태로 pytest하는 것 같다?!
git status git add . git commit -am "feat: implementing data interfaces" git commit -am "feat: implementing data interfaces" -
git push는 현재 로그인된 vscode에서 하고 있음.
-
github에 들어가보면,
Compare & pull request가 떠있더라도PR탭 > new PR로 들어가는 버릇을 들여보자.
- Comparing change까지 들어가서 코드를 확인하고
Able to merge및세부코드를 확인하고 직접 Create PR까지 가자
- merge후 master에 반영되었는지까지 확인하자
vscode 설정
- 캐쉬파일 안보이기
"files.exclude": {
"**/__pycache__": true,
"**/.pytest_cache": true
}
-
tab시 space로 입력되기
-
탐색기 열기 단축키 :
shift + alt + R- 파일: 파일 탐색기에 표시
test정리
-
repo_insert_X
- id제외 faker + insert메서드 -> new_dto
- new_dto속 배정id + engine db select -> query_data -> engine db delete
- assert new_dto.필드 == query_data필드 비교
-
repo_select_X
- id포함 faker -> entity모델 객체
- id포함 재료들 + engine db insert -> db데이터만들어놓기
- id, fk재료들 + select메서드 -> List[entity모델객체들]
- engine db delete
status_code
-
422: validate_entry실패하는 query 속 param들 -> usecase메서드의 결과물 response의 [“Success”]가 False- 필수param(dict속 필드)이 빠졌을 경우(존재검증) or 필수param이 validate_entry실패할 경우
if reponse["Success"] is False: -
400: query속 param들이 필요한 controller인데 http_request안에 아예 존재도 안했다면, 400 Bad Request에러- http_request에 필수param을 포함한 .query or .body가 아예 날라오지도 않았을 경우
if http_request.query: # if query # if not query else:if http_request.body: # if body # if not body else: